Overview
Cat #:
C-280
Lyophilized Powder yes
Origin Synthetic peptide
MW: 1883 Da
Purity: >99% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 0.1-10 μM.
Sequence CCNCSSKWCRDHSRCC.
Modifications Disulfide bonds between Cys1-Cys9, Cys2-Cys15 and Cys4 -Cys16. Cys16 - C-terminal amidation.
Molecular formula C70H100N28O22S6.
Activity μ-Conotoxin KIIIA specifically and in some cases reversibly blocks TTX-sensitive mammalian voltage-dependent Na+ (NaV) channels1.
References-Activity
- Zhang, M.M. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 30699.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Any aqueous buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to two weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
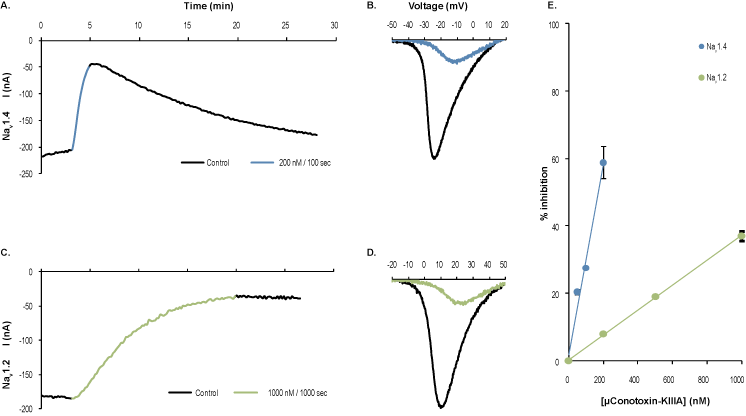 Alomone Labs μ-Conotoxin KIIIA differentially inhibits NaV1.4 and NaV1.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of μ-Conotoxin KIIIA (#C-280) action on NaV1.4 channels. Current amplitudes were plotted as a function of time. Oocyte membrane potential was held at -100 mV and 50 ms ramp to +50 mV was delivered every 10 seconds. 200 nM μ-Conotoxin KIIIA was perfused during the period marked in blue (100 seconds exposure). B. Example traces of NaV1.4 channel currents before (black) and during (blue) μ-Conotoxin KIIIA application. C. Time course of μ-Conotoxin KIIIA action on NaV1.2 channels. 1000 nM μ-Conotoxin KIIIA were perfused during the period marked in green (1000 seconds exposure). D. Example traces of NaV1.2 channel currents before (black) and during (green) μ-Conotoxin KIIIA application. E. Dose-response curves for NaV1.4 and NaV1.2 inhibition (upon 100 seconds exposure to the toxin; such as in A.).
Alomone Labs μ-Conotoxin KIIIA differentially inhibits NaV1.4 and NaV1.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of μ-Conotoxin KIIIA (#C-280) action on NaV1.4 channels. Current amplitudes were plotted as a function of time. Oocyte membrane potential was held at -100 mV and 50 ms ramp to +50 mV was delivered every 10 seconds. 200 nM μ-Conotoxin KIIIA was perfused during the period marked in blue (100 seconds exposure). B. Example traces of NaV1.4 channel currents before (black) and during (blue) μ-Conotoxin KIIIA application. C. Time course of μ-Conotoxin KIIIA action on NaV1.2 channels. 1000 nM μ-Conotoxin KIIIA were perfused during the period marked in green (1000 seconds exposure). D. Example traces of NaV1.2 channel currents before (black) and during (green) μ-Conotoxin KIIIA application. E. Dose-response curves for NaV1.4 and NaV1.2 inhibition (upon 100 seconds exposure to the toxin; such as in A.).
References - Scientific background
- Bulaj, G. et al. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 7259.
- Zhang, M.M. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 30699.
- Norton, R.S. (2010) Molecules 15, 2825.
Scientific background µ-Conotoxin KIIIA is a toxin originally isolated from the venom of Conus Kinoshitai1. µ-Conotoxin KIIIA specifically, and in some cases reversibly, blocks TTX-sensitive mammalian voltage-dependent Na+ (NaV) channels2. In addition, µ-Conotoxin KIIIA was found to act as an effective analgesic in an inflammatory pain assay in mice in vivo2,3.
Target TTX-sensitive Na+ channels
Peptide Content: 100%
Lyophilized Powder
µ-Conotoxin KIIIA (#C-280) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 08/01/2025
Applications
Citations
Citations

