Overview
- Wilson, S.P. and Kirshner, N. (1977) J. Neurochem. 28, 687.
- Garcia-Guzman, M. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 647.
- McCann, C.M. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5149.
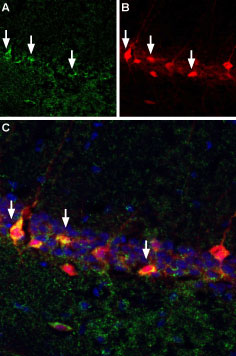 Bungarotoxin binding sites co-localize with GABAergic neurons expressing parvalbumin in mouse hippocampal CA1 region.A. Free floating mouse brain sections were incubated with α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B), (1:10,000) followed by streptavidin-Alexa 488 (green). B. Same sections were stained with anti-parvalbumin, followed by goat anti-mouse labeled with Texas red isothiocyanate (TRITC). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates sites of colocalization (vertical arrows) confirming reports that a subset of hippocampal interneurons express nAChR α7. DAPI is used as the counterstain.
Bungarotoxin binding sites co-localize with GABAergic neurons expressing parvalbumin in mouse hippocampal CA1 region.A. Free floating mouse brain sections were incubated with α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B), (1:10,000) followed by streptavidin-Alexa 488 (green). B. Same sections were stained with anti-parvalbumin, followed by goat anti-mouse labeled with Texas red isothiocyanate (TRITC). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates sites of colocalization (vertical arrows) confirming reports that a subset of hippocampal interneurons express nAChR α7. DAPI is used as the counterstain. Indirect flow cytometry of α-Bungarotoxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B) + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.
Indirect flow cytometry of α-Bungarotoxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B) + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.
___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM α-Bungarotoxin (#B-100) + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate.
___ PC-12 cells + 2 µg/ml Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugate. Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin inhibits muscle nAChR channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of muscle nAChR (α1/β1/γ/δ) current recording. Membrane potential was held at -80 mV and stimulated by perfused with a solution containing 100 µM ACh and 3 μM PNU-120596 every 100 sec. 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B) was applied (green) during the ACh application for 5.5 min and inhibited channel current, as indicated. B. Superimposed examples of muscle nAChR current in the absence (black) and presence (green) of 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (taken from the experiment in A).
Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin inhibits muscle nAChR channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of muscle nAChR (α1/β1/γ/δ) current recording. Membrane potential was held at -80 mV and stimulated by perfused with a solution containing 100 µM ACh and 3 μM PNU-120596 every 100 sec. 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B) was applied (green) during the ACh application for 5.5 min and inhibited channel current, as indicated. B. Superimposed examples of muscle nAChR current in the absence (black) and presence (green) of 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (taken from the experiment in A).
- Ohta, M. et al. (1987) FEBS Lett. 222, 79.
- Wilson, P.T. et al. (1988) Mol. Pharmacol. 34, 643.
- Wilson, S.P. and Kirshner, N. (1977) J. Neurochem. 28, 687.
- Garcia-Guzman, M. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 647.
- McCann, C.M. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5149.
α-Bungarotoxin isoform A31 is a 74 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from the venom of the banded krait snake, Bungarus multicinctus1.
α-Bungarotoxin blocks postsynaptic neuromuscular transmission via competitive inhibition of nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChRs) with an IC50 of 3.5 x 10-10 M, thereby preventing the depolarizing action on postsynaptic membranes and blocking neuromuscular transmission2.
The toxin is selective for α7 receptors (IC50 value of 1.6 nM) and α3/β4 receptors (IC50 value of >3 µM)3,4.
α-Bungarotoxin also binds to and blocks a subset of GABAA receptors (GABAARs) that contain the GABAAR β3 subunit. In particular, α-Bungarotoxin blocks GABAARs that contain interfaces between adjacent β3 subunits5.
α-Bungarotoxin-Biotin (#B-100-B) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active conjugated peptide toxin.
We gladly take on collaboration projects. Please Contact Us.

