Overview
Disulfide bonds between: Cys5-11, Cys6-16
Cys16 - C-terminal amidation
Pro3 - Hydroxyproline
E1 - Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid
- Echterbille, J. et al. (2017) Toxicon 130, 1.
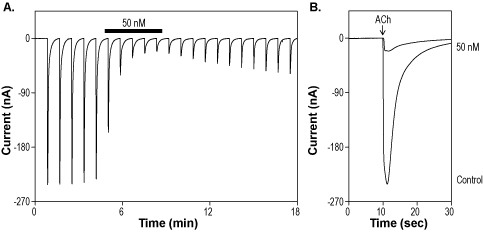 Alomone Labs α-Conotoxin EIIB inhibits muscle nicotinic ACh receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of α-Conotoxin EIIB (#STC-230) inhibition of α1/β1/γ/δ nAChR. Currents were elicited every 50 sec by transient application of 20 µM ACh, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV, and inhibited by 50 nM α-Conotoxin-EIIB (horizontal bar). B. Superimposed traces of α1/β1/γ/δ nAChR currents upon application of control and of 50 nM α-Conotoxin-EIIB (taken from the recording in A).
Alomone Labs α-Conotoxin EIIB inhibits muscle nicotinic ACh receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of α-Conotoxin EIIB (#STC-230) inhibition of α1/β1/γ/δ nAChR. Currents were elicited every 50 sec by transient application of 20 µM ACh, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV, and inhibited by 50 nM α-Conotoxin-EIIB (horizontal bar). B. Superimposed traces of α1/β1/γ/δ nAChR currents upon application of control and of 50 nM α-Conotoxin-EIIB (taken from the recording in A).
- Echterbille, J. et al. (2017) Toxicon 130, 1.
- Benie, A.J. et al. (2000) FEBS Lett. 476, 287.
- Lustig, L.R. et al. (2006) Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 288, 424.
α-Conotoxin EIIB is a peptide toxin originally isolated from Conus ermineus (Atlantic fish-hunting cone) venom. It is a potent α1/β1/δ/γ nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist and displays a Ki of 2.2 ± 0.7 nM1. The peptide toxin is stabilized by six hydrogen bonds and disulfides between residues 2 and 7 and 3 and 132.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are ionotropic multisubunit, neurotransmitter-gated receptors of the cholinergic system. They are assembled from one or more α subunits (α1-α10) alone or together with one or more β subunits (β1–β4)3. Other subunits also co-assemble in the formation of the receptor channel.
α-Conotoxin EIIB (#STC-230) is a highly pure, synthetic and biologically active peptide toxin.

