Overview
- Wilson, S.P. and Kirshner, N. (1977) J. Neurochem. 28, 687.
- Garcia-Guzman, M. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 647.
- McCann, C.M. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5149.
Centrifuge the vial before adding solvent (10,000 x g for 5 minutes). The lyophilizate may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Tap the vial to aid in dissolving the lyophilized product. Tilt and gently roll the liquid over the walls of the vial. Avoid vigorous vortexing. Light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed.
Soluble in pure water at high-micromolar concentrations (50 µM - 1 mM). For long-term storage in solution, it is recommended to prepare a stock solution by dissolving the product in double distilled water (ddH2O) at a concentration between 100-1000x of the final working concentration. Divide the stock solution into small aliquots and store at -20°C. Before use, thaw the relevant vial(s) and dilute to the desired working concentration in your working buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations at 10,000 x g for 5 minutes before use. It is recommended to prepare fresh solutions in working buffers just before use. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain biological activity. Avoid exposure to light.
 Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 in whole mount staining of mouse Gastrocnemius muscle.Whole mount staining of mouse Gastrocnemius muscle stained with the neuromuscular junction marker α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG), (green) at 1:50 (A) and 1:100 (B) ratios.
Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 in whole mount staining of mouse Gastrocnemius muscle.Whole mount staining of mouse Gastrocnemius muscle stained with the neuromuscular junction marker α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG), (green) at 1:50 (A) and 1:100 (B) ratios.
The images were taken using Nikon Epifluorescence microscopy at X100 magnification and are a kind gift from Dr. Eran Perlsson, Dept. of Physiology and Pharmacology, Tel-Aviv University. Direct flow cytometry of α-Bungarotoxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
Direct flow cytometry of α-Bungarotoxin in live intact rat PC-12 cells.___ PC-12 cells.
___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM α-Bungarotoxin (#B-100).
___ PC-12 cells + 1 µM α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG).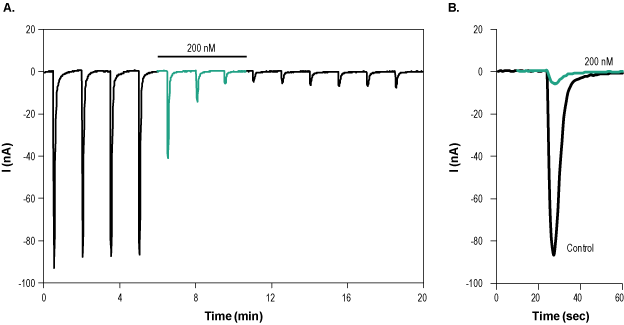 Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 inhibits α7 nAChR heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of α7 nAChR current recording. Membrane potential was held at -60 mV and constantly perfused with a solution containing 3 μM PNU-120596. 1 mM ACh was applied for 2 seconds every 90 seconds, in order to stimulate the channel’s current. 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG) was applied (green) during the ACh application and inhibited channel current. B. Superimposed examples of α7 nicotinic ACh current in the absence (black) and presence (green) of 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (taken from the experiment in A).
Alomone Labs α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 inhibits α7 nAChR heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of α7 nAChR current recording. Membrane potential was held at -60 mV and constantly perfused with a solution containing 3 μM PNU-120596. 1 mM ACh was applied for 2 seconds every 90 seconds, in order to stimulate the channel’s current. 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG) was applied (green) during the ACh application and inhibited channel current. B. Superimposed examples of α7 nicotinic ACh current in the absence (black) and presence (green) of 200 nM α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (taken from the experiment in A).
- Ohta, M. et al. (1987) FEBS Lett. 222, 79.
- Wilson, P.T. et al. (1988) Mol. Pharmacol. 34, 643.
- Wilson, S.P. and Kirshner, N. (1977) J. Neurochem. 28, 687.
- Garcia-Guzman, M. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 647.
- McCann, C.M. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5149.
α-Bungarotoxin isoform A31 is a 74 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from the venom of the banded krait snake, Bungarus multicinctus1.
α-Bungarotoxin blocks postsynaptic neuromuscular transmission via competitive inhibition of nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChRs) with an IC50 of 3.5 x 10-10 M, thereby preventing the depolarizing action on postsynaptic membranes and blocking neuromuscular transmission2.
The toxin is selective for α7 receptors (IC50 value of 1.6 nM) and α3/β4 receptors (IC50 value of >3 µM)3,4.
α-Bungarotoxin also binds to and blocks a subset of GABAA receptors (GABAARs) that contain the GABAAR β3 subunit. In particular, α-Bungarotoxin blocks GABAARs that contain interfaces between adjacent β3 subunits5.
α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-488 (#B-100-AG) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active conjugated peptide toxin.
✓ Localization and distribution
✓ Live cell imaging
✓ Single cell detection
✓ Direct flow cytometry
We gladly take on collaboration projects. Please Contact Us.
Applications
Citations
- Liu, Y. et al. (2020) Stem Cell Reports. 15, 941.
- Zhang, J. J. et al. (2018) CNS Neurosci Ther. 24, 1163.
- Li, B. et al. (2020) Neural Regen Res. 15, 1678.
- Lenzi, J. et al. (2016) Stem Cell Res. 17, 140.

