Overview
7-Chlorokynurenic acid (7-CKA), a derivative of kynurenic acid, is a potent and selective antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. 7-CKA acts and binds with high affinity to the glycine binding site located on the NMDA receptor. This compound has neuroprotective, antinociceptive and anticonvulsive effects lacking the ability to penetrate the blood-brain-barrier and has therapeutic potential in some types of epilepsy1-3. Several studies that conducted radioligand binding experiments showed that 7-chlorokynurenic acid binds to the strychnine-glycine binding site with high affinity (IC50 value of 0.56 μM)5.
Several studies have shown that acute administration of 7-CKA can produce rapid antidepressant-like effects without showing addictive potential2. It seems that inhibition of the phospho-glycogen synthase kinase-3β pathway and activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin in the medial prefrontal cortex are connected to the 7-CKA rapid behavioural response2.
NMDA receptors play an important role in a variety of cellular processes and brain functions such as synaptic plasticity, addiction and stroke. NMDA receptors mediate several physiological functions including learning and memory formation, they play a role in glutamate excitotoxicity and are involved in many neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease4.
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Biological Activity
- Green, T. et al. (2002) Mol. Pharmacol. 61, 326.
Solubility and Storage
Applications
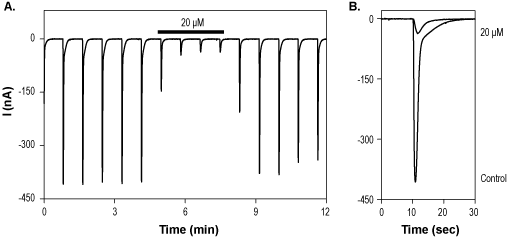 Alomone Labs 7-Chlorokynurenic acid inhibits NMDA (NR1+NR2A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of NMDA currents elicited with 10 µM glutamate and 10 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV. 20 µM 7-Chlorokynurenic acid (#C-285), applied for 2.5 min as indicated, inhibited current amplitude. B. Superimposed current traces taken from the experiment described in A.
Alomone Labs 7-Chlorokynurenic acid inhibits NMDA (NR1+NR2A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of NMDA currents elicited with 10 µM glutamate and 10 µM glycine every 50 sec, while membrane potential was held at -80 mV. 20 µM 7-Chlorokynurenic acid (#C-285), applied for 2.5 min as indicated, inhibited current amplitude. B. Superimposed current traces taken from the experiment described in A.

