Overview
- McGaraughty, S. et al. (2010) Mol. Pain 6, 14.
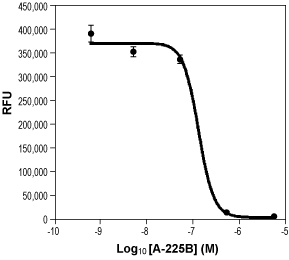 Alomone Labs A 967079 inhibits Allyl isothiocyanate induced calcium signal in TRPA1 expressing cells.Dose-response curve for the inhibition of human TRPA1 expressing HEK-293 cells loaded with Calcium 5 dye for changes in intracellular Ca2+ measurements. Allyl isothiocyanate (100 µM)-induced calcium signal was completely inhibited by 0.5 µM A 967079 (#A-225), with an estimated IC50 of about 120 nM.
Alomone Labs A 967079 inhibits Allyl isothiocyanate induced calcium signal in TRPA1 expressing cells.Dose-response curve for the inhibition of human TRPA1 expressing HEK-293 cells loaded with Calcium 5 dye for changes in intracellular Ca2+ measurements. Allyl isothiocyanate (100 µM)-induced calcium signal was completely inhibited by 0.5 µM A 967079 (#A-225), with an estimated IC50 of about 120 nM.
The transient receptor potential (TRP) channel is one of the largest families of cation channels1.
TRPA1 is expressed in sensory and nociceptive neurons and has a significant role in the inflammatory response. Bradykinin and histamine receptors induce TRPA1 activity. It has been found that TRPA1 deficient mice do not develop an elevated mechanical and thermal pain response following bradykinin injection. This suggests that TRPA1 has a vital role in bradykinin signaling pathways2.
TRPA1 also plays a role in acute and chronic respiratory disease pathophysiology. Prolonged exposure to TRPA1 agonists such as chlorine and aldehydes can cause reactive airway dysfunction syndrome characterized by symptoms such as wheezing, cough and dyspnea. In view of this, TRPA1 is a potential target in airway anti-inflammatory research3.
A 967079 is a TRPA1 blocker and has an IC50 value of 67 and 289 nM for human and rat TRPA1 receptors respectively.

