Overview
- Broom, D.C. et al. (2008) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 327, 620.
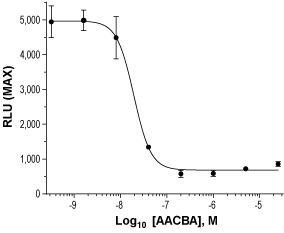 Alomone Labs AACBA hydrochloride inhibits human P2X7 receptors expressed in HEK-293 cells.Dose-response curve of hP2X7 inhibition by AACBA hydrochloride (#A-410). Cells were loaded with Fluo-8 NW dye, incubated with increasing concentrations of AACBA hydrochloride, and stimulated with 80 µM BzATP. Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following agonist application were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™. IC50 was calculated at 19.3 nM.
Alomone Labs AACBA hydrochloride inhibits human P2X7 receptors expressed in HEK-293 cells.Dose-response curve of hP2X7 inhibition by AACBA hydrochloride (#A-410). Cells were loaded with Fluo-8 NW dye, incubated with increasing concentrations of AACBA hydrochloride, and stimulated with 80 µM BzATP. Changes in intracellular Ca2+ following agonist application were detected as changes in maximum relative fluorescence (RLU) using FLIPRTETRA™. IC50 was calculated at 19.3 nM.
- Broom, D.C. et al. (2008) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 327, 620.
- Pijacka, W. et al. (2016) Nat. Med. 10, 1151.
AACBA hydrochloride is a potent and selective antagonist of P2X7 receptors. It inhibits human and rat P2X7 receptors with IC50 values of 18 nM and 29 nM, respectively1.
AACBA reduces interleukin-6 release in a dose-dependent manner and prevents or reverses carrageenan-induced paw edema and mechanical hypersensitivity in acute in vivo models of pain and inflammation1.
P2X receptors are a family of ion channels gated by ATP, a ubiquitous energy donor and receptor ligand in living cells. P2X receptors are widely expressed in neuronal, muscular, epithelial and immune cells and play a pivotal role in models of various pain conditions. P2X7 receptor mediates the release of proinflammatory cytokines known to have roles in inflammatory/immune conditions and pain1,2.
AACBA hydrochloride (#A-410) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

