Overview
|
| Bioz Stars Product Rating | |
| The world's only objective ratings for scientific research products | |
| Mentions | |
| Recency | |
| View product page > | |
Agitoxin-1 (#STA-150) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.
Applications
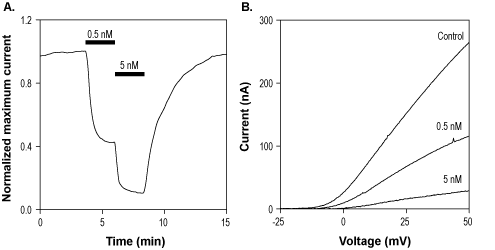 Alomone Labs Agitoxin-1 blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Agitoxin-1 (#STA-150) inhibition of KV1.3 current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV. Current elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec was significantly and reversibly inhibited by 2 min applications of 0.5 nM and 5 nM Agitoxin-1, as indicated. B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current before and after application of 0.5 nM and 5 nM Agitoxin-1, taken from the recording in A.
Alomone Labs Agitoxin-1 blocks KV1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Representative time course of Agitoxin-1 (#STA-150) inhibition of KV1.3 current. Membrane potential was held at -100 mV. Current elicited by a 100 ms voltage ramp to +60 mV every 10 sec was significantly and reversibly inhibited by 2 min applications of 0.5 nM and 5 nM Agitoxin-1, as indicated. B. Superimposed traces of KV1.3 current before and after application of 0.5 nM and 5 nM Agitoxin-1, taken from the recording in A.
Citations (6)
- Meneses, D. et al. (2016) Neural Plast. 2016, 8782518.
- Druzin, M. et al. (2011) PLoS ONE 6, e20213.
- Al-Sabi, A. et al. (2010) J. Gen. Physiol. 136, 273.
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Biological Activity
Solubility and Storage
Scientific Background
Agitoxins are peptide toxins originally isolated from L. quinquestriatus hebraeus scorpion venom. This group of toxins blocks potassium (K⁺) channels and has a central role in the investigation and understanding of the physiological importance of K+ channels and their function in membrane biophysics1.
Agitoxins 1, 2 and 3 have been isolated and characterized. Each toxin is comprised of 38 amino acids. They are highly homologous and differ only in the identity of the residues at positions 7, 15, 29 and 31.
Agitoxins appear to be specific for the Shaker K+ channel of Drosophila melanogaster and many of the mammalian homologues of Shaker. Agitoxin-1 blocks the Shaker channel in a stoichiometry of one to one, it binds the channel site in the extracellular vestibule and prevents ion conduction by occluding the pore2.
Using scorpion toxins for molecular dissection of ion channels has led to direct evidence that specific mutations can be correlated to changes in the propagation and conduction of electrical impulses in the body3.
- Bergeron, Z.L. and Bingham, J.P. (2012) Toxins 4, 1082.
- Garcia, M.L. et al. (1994) Biochemistry 33, 6834.
- Aggarwal, S.K. and MacKinnon, R. (1996) Neuron 6, 1169.

