Overview
- Coutinho, D.C. et al. (2013) J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 15, 480.
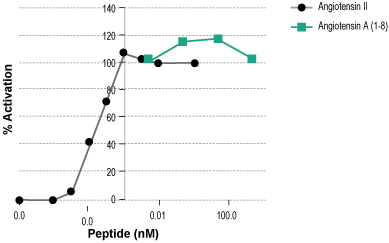 Alomone Labs Angiotensin A (1-8) activates AT1R expressed in CHO-K1-mt Aequorin-Gα16 cells.Ca2+ response was detected by measuring aequorin-derived fluorescence following application of Angiotensin A )1-8) (#SPA-105) or Angiotensin II (#GPA-100) at different concentrations.
Alomone Labs Angiotensin A (1-8) activates AT1R expressed in CHO-K1-mt Aequorin-Gα16 cells.Ca2+ response was detected by measuring aequorin-derived fluorescence following application of Angiotensin A )1-8) (#SPA-105) or Angiotensin II (#GPA-100) at different concentrations.
- Coutinho, D.C. et al. (2013) J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 15, 480.
- Brasch, H. et al. (1993) Hypertension 22, 699.
Angiotensin A (1-8) is an angiotensin II derivative, a vasoconstrictor peptide of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) that acts as an angiotensin receptor type 1 and 2 (AT1R and AT2R) agonist.
This peptide was first discovered in the human plasma and the sole difference between Ang A and Ang II is Ala1 residue instead of Asp1. Ang A is synthesized by enzymatic decarboxylation of Asp1 of the Ang II sequence1.
Angiotensin I is metabolized to the vasoconstricting octapeptide angiotensin II by a circulating converting enzyme (ACE) by removal of two C-terminal residues. It's a natural hormone which the body produces in order to maintain normal regulation of cardiovascular function.
Ang II is a primary effector peptide of the RAS in a variety of tissues and is a major target for blood pressure lowering drugs2.
Studies show that Ang A has the ability to elicit pressor and renal vasoconstrictor responses in normotensive and hypertensive rats. In isolated perfused rat kidney, the peptide causes a vasoconstrictive effect dependent on AT1 receptors1.
Angiotensin A (1-8) (#SPA-105) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide.

