Overview
- Peptide (C)DAGNSSWNGTEAPG, corresponding to amino acid residues 7-20 of rat α2A-adrenoceptor (Accession P22909). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain lysate (1:200).
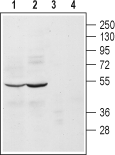 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1, 2. Anti-α2A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-020), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1, 2. Anti-α2A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-020), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-α2A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with α2A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR020).
- Rat cerebellum and hypothalamus sections (1:250).
Adrenergic receptors (also called adrenoceptors) are the receptors for the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline (called epinephrine and norepinephrine in the United States). Adrenaline and noradrenaline play important roles in the control of blood pressure, myocardial contractile rate and force, airway reactivity, and a variety of metabolic and central nervous system functions.
Adrenergic receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily of membrane proteins. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular N-terminus, and a cytoplasmic C- terminus.
Adrenoceptors are divided into three types: α1, α2 and β-adrenoceptors. Each type is further divided into at least three subtypes: α1A, α1B, α1D, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2, β31,2. Adrenoceptors are expressed in nearly all peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system1,2.
In general, the pharmacological properties of each subtype are quite homogenous across different species. However, this is not the case for the α2A subtype which was first isolated from human platelets3. This subtype shows different pharmacological properties from that of mouse and rat. For this reason, until molecular techniques significantly advanced, it was believed that human α2A and that of mouse and rat (termed α2D) were two different subtypes. Today, it is accepted that these two subtypes are in fact one gene product and is generally termed α2A. One of the main differences between this subtype from the different organisms is its affinity for yohimbine and rauwolscine; rat and mouse α2A displays less affinity compared to human3,4.
