Overview
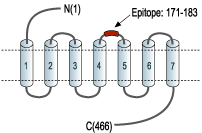
- Peptide EDETI*SQINEEPG(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 171-183 of human α1A-adrenoceptor with replacement of cysteine 176 (C176) with serine (*S) (Accession P35348). 2nd extracellular loop.
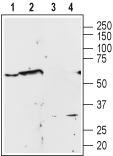 Western blot analysis of Human PC3 prostate carcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membrane (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-015), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of Human PC3 prostate carcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membrane (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-015), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR015).
 Expression of α1A-Adrenergic receptor in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-015), (1:100). A. α1A-adrenoceptor (green) appears in fibers of Bergmann glia (triangle points at an example). B. S100β (red), a marker of Bergmann glia, is stained in the same section. C. Merge of the images demonstrates expression of α1A-adrenoceptor in fibers of Bergmann glia. α1A-adrenoceptor is also expressed in cells in the molecular layer that are s100β negative (arrow points at an example). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of α1A-Adrenergic receptor in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-015), (1:100). A. α1A-adrenoceptor (green) appears in fibers of Bergmann glia (triangle points at an example). B. S100β (red), a marker of Bergmann glia, is stained in the same section. C. Merge of the images demonstrates expression of α1A-adrenoceptor in fibers of Bergmann glia. α1A-adrenoceptor is also expressed in cells in the molecular layer that are s100β negative (arrow points at an example). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- IUPHAR RECEPTOR DATABASE | ADRENOCEPTORS.
- Piascik, M.T. and Perez, D.M. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298, 403.
- Perez, D.M. et al. (1993) Mol Pharmacol 44, 784.
- Minneman, K.P. (1988) Pharmacol. Rev. 40, 87.
Adrenergic receptors (also called adrenoceptors) are the receptors for the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline (called epinephrine and norepinephrine in the United States). Adrenaline and noradrenaline play important roles in the control of blood pressure, myocardial contractile rate and force, airway reactivity, and a variety of metabolic and central nervous system functions.
Adrenergic receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily of membrane proteins. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, and a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus.
Adrenoceptors are divided into three types: α1, α2 and β adrenoceptors. Each type is further divided into at least three subtypes: α1A, α1B, α1D, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2, β3.1,2 They are expressed in nearly all peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system.1,2
All α1-adrenoceptors (α1-ARs) activate phospholipases C and A2.3 In addition to mobilizing intracellular calcium, the α1-ARs have also been shown to activate calcium influx via voltage-dependent and -independent calcium channels.4
The α1A-ARs have at least nine known alternative spliced isoforms. They are the most abundant adrenergic receptor in the brain, and are considered postsynaptic receptors. α1A-ARs are also expressed in the heart, liver and prostate.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human α1A-adrenergic receptor. Anti-α1A-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-015) can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize α1A-adrenoceptor from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197. - Rat brain sections (1:200).
Igata, S. et al. (2014) J. Neurophysiol. 111, 777.
- Human urothelial cells.
Matos, R. et al. (2016) Acta Physiol. 218, 265.
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197. - Human urothelial cells.
Matos, R. et al. (2016) Acta Physiol. 218, 265. - Rat brain sections (1:200).
Igata, S. et al. (2014) J. Neurophysiol. 111, 777.

