Overview
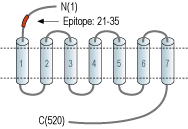
- Peptide (C)KNANFTGPNQTSSNS, corresponding to amino acid residues 21-35 of human α1B-adrenoceptor (Accession P35368). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of α1B-Adrenoceptor in rat brain (lanes 1 and 3), rat kidney (lanes 2 and 4) and GH3 cell line (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-018), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of α1B-Adrenoceptor in rat brain (lanes 1 and 3), rat kidney (lanes 2 and 4) and GH3 cell line (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-018), (1:200).
3,4,6. Anti-α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR018).
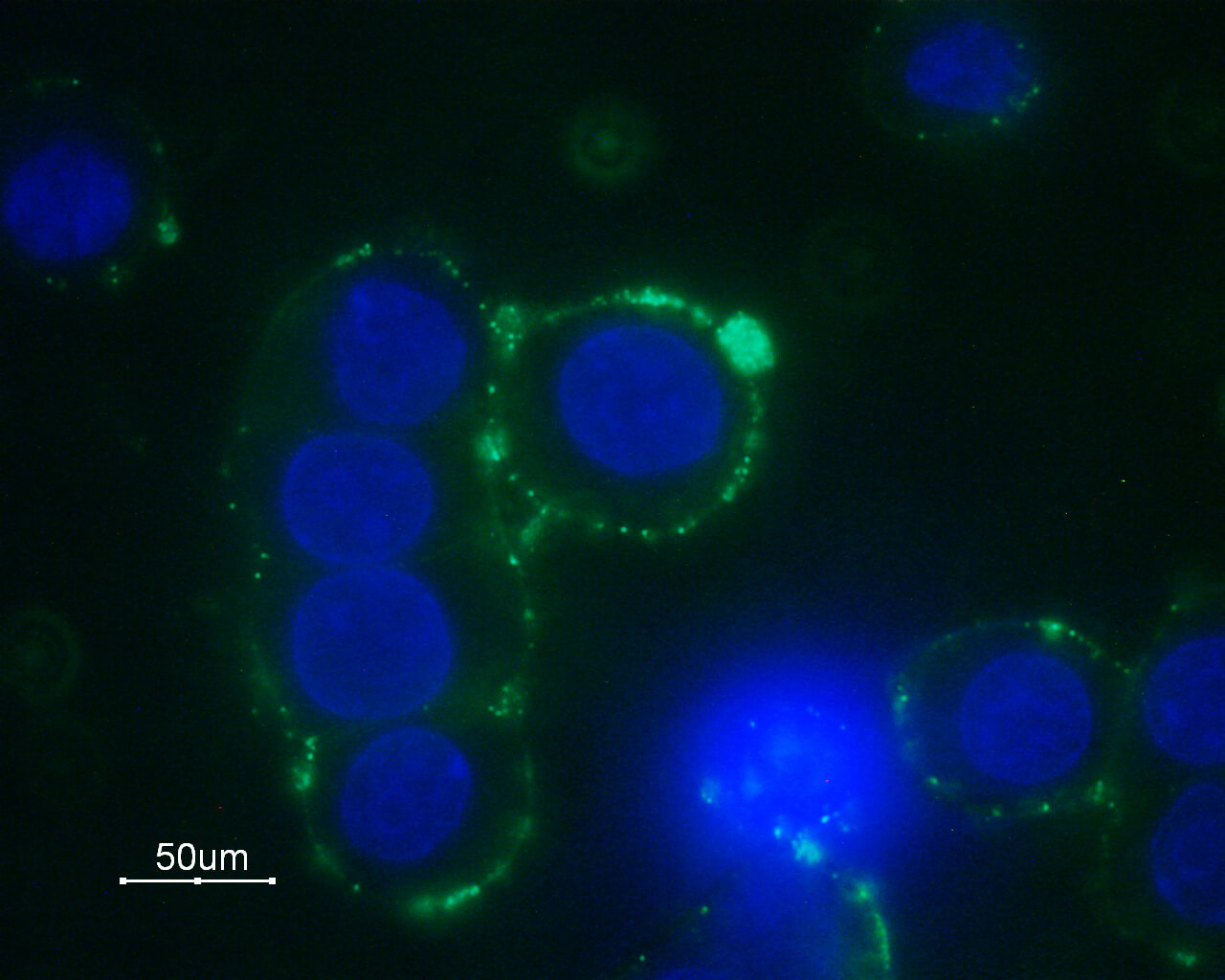 Expression of α1B-Adrenoceptor in GH3 cellsCell surface detection of α1B-Adrenoceptor in living GH3 cells with Anti-α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-018), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Nuclear staining of cells using the DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (blue).
Expression of α1B-Adrenoceptor in GH3 cellsCell surface detection of α1B-Adrenoceptor in living GH3 cells with Anti-α1B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-018), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Nuclear staining of cells using the DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (blue).
- IUPHAR RECEPTOR DATABASE | ADRENOCEPTORS
- Piascik, M.T .and Perez, D.M. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298, 403.
- Perez, D.M. et al. (1993) Mol. Pharmacol. 44, 784.
- Minneman, K.P. (1988) Pharmacol. Rev. 40, 87.
- Schwinn, D.A. et al. (2004) Mayo Clin. Proc. 79, 1423.
Adrenergic receptors (also called adrenoceptors) are the receptors for the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline (called epinephrine and norepinephrine in the United States). Adrenaline and noradrenaline play important roles in the control of blood pressure, myocardial contractile rate and force, airway reactivity, and a variety of metabolic and central nervous system functions.
Adrenergic receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily of membrane proteins. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, and a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus.
Adrenoceptors are divided into three types: α1, α2 and β adrenoceptors. Each type is further divided into at least three subtypes: α1A, α1B, α1D, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2, β3.1,2 They are expressed in nearly all peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system.1,2
All α1-adrenoceptors (α1-ARs) activate phospholipases C and A2.3 In addition to mobilizing intracellular calcium, the α1-ARs have also been shown to activate calcium influx via voltage-dependent and -independent calcium channels.4
α1B-Adrenergic receptor populations are greatest in the spleen, kidney, cerebellum, and fetal brain.5
α1B-Adrenoceptor causes contraction of smooth muscle cells and thereby controls vascular tone, blood pressure, and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis.5
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-α1B–Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-018) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human α1B-adrenoceptor. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, live cell imaging and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize α1B-adrenoceptor from human, rat and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197.
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197.


