Overview
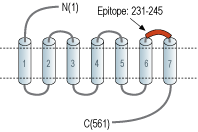
- Peptide (C)EPVPPDERF*SGITEE, corresponding to amino acid residues 231-245 of rat α1D-adrenoceptor with replacement of cysteine 240 (C240) with serine (*S) (Accession P23944). 3rd extracellular loop.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain stem (lanes 1 and 3), mouse brain (lanes 2 and 4), SH-SY5Y (lanes 5 and 7) and Jurkat (lanes 6 and 8) lysates:1,2,5,6. Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain stem (lanes 1 and 3), mouse brain (lanes 2 and 4), SH-SY5Y (lanes 5 and 7) and Jurkat (lanes 6 and 8) lysates:1,2,5,6. Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019), (1:200).
3,4,7,8. Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR019).
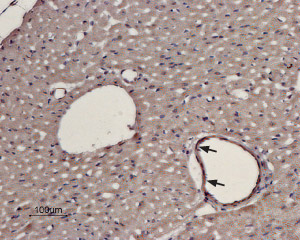 Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat heartImmunohistochemical staining of rat heart paraffin embedded sections using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019), (1:100). α1D-Adrenoceptor is expressed in cardiomyocytes of the myocardium and in the smooth muscle of the blood vessels (arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat heartImmunohistochemical staining of rat heart paraffin embedded sections using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019), (1:100). α1D-Adrenoceptor is expressed in cardiomyocytes of the myocardium and in the smooth muscle of the blood vessels (arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain. Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat neocortexImmunohistochemical staining of α1D-adrenoceptor in rat neocortex using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019). A. Most intense staining of α1D-adrenoceptor (green) appears in apical dendrites (thin horizontal arrows) but also in the soma (thick horizontal arrow). Few cortical interneurons express α1D-adrenoceptor. B. The same section was also stained for parvalbumin and one cell (marked with a vertical arrow) also expresses α1D-adrenoceptor.
Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat neocortexImmunohistochemical staining of α1D-adrenoceptor in rat neocortex using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019). A. Most intense staining of α1D-adrenoceptor (green) appears in apical dendrites (thin horizontal arrows) but also in the soma (thick horizontal arrow). Few cortical interneurons express α1D-adrenoceptor. B. The same section was also stained for parvalbumin and one cell (marked with a vertical arrow) also expresses α1D-adrenoceptor.
 Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of α1D-Adrenoceptor in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019) (1:100) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. B. Merge of A and live view of the cells.
Expression of α1D-Adrenoceptor in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of α1D-Adrenoceptor in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019) (1:100) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. B. Merge of A and live view of the cells.
- IUPHAR RECEPTOR DATABASE | ADRENOCEPTORS
- Piascik, M.T .and Perez, D.M. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298, 403.
- Chen, Z.J. and Minneman, K.P. (2005) Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26, 1281.
- Tanoue, A. et al. (2002) J. Clin. Invest. 109, 765.
- Chen, Q. et al. (2005) J. Urol. 174, 370.
Adrenergic receptors (also called adrenoceptors) are the receptors for the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline (called epinephrine and norepinephrine in the United States). Adrenaline and noradrenaline play important roles in the control of blood pressure, myocardial contractile rate and force, airway reactivity, and a variety of metabolic and central nervous system functions.
Adrenergic receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily of membrane proteins. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, and a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus.
Adrenoceptors are divided into three types: α1, α2 and β-adrenoceptors. Each type is further divided into at least three subtypes: α1A, α1B, α1D, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2, β31,2. The adrenoceptors are expressed in nearly all peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system1,2.
α1-Adrenergic receptors play an important role in the physiological response to epinephrine and norepinephrine, particularly in the cardiovascular system. All three cloned α1 receptors (α1A, α1B, and α1D) couple to Gq/11. While their cellular distribution is clear, their functional role is less so due to a lack of specific agonists/antagonists3.
As these receptors lack specific agonists/antagonists, knock-out (KO) studies in mice have shed significant light on their cellular role. Individual α1-adrenoceptor KO mice do not display physical abnormalities in general. Similar KO studies indicate that all α1 subtypes seem to be involved in the regulation of blood pressure3. Also, studies indicate that α1D-adrenoceptor seems to play an important role in aortic contraction4, renal function, nociception, basal locomotor activity3 as well as bladder contraction5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
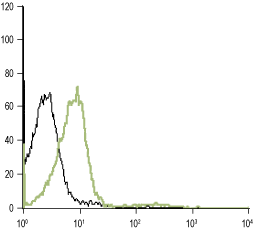
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat α1D-adrenergic receptor. Anti-α1D-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-019) can be used in western blot, indirect flow cytometry and immunohistochemical applications. It has been designed to recognize α1D-adrenoceptor from mouse, rat and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197.
- Rat trigeminal ganglia sections.
Benbow, T. et al. (2020) Neuropharmacology 175, 108197.