Overview
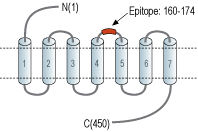
- Peptide (C)RPEPRGLPQ*SELNQE, corresponding to amino acid residues 160-174 of rat α2B-adrenoceptor with replacement of cysteine 169 (C169) with serine (*S) (Accession P19328). 2nd extracellular loop.
 Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 5), lung (lanes 2 and 6), liver (lanes 3 and 7) lysates and rat skeletal muscle membranes (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 5), lung (lanes 2 and 6), liver (lanes 3 and 7) lysates and rat skeletal muscle membranes (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR021).
 Expression of α2B-Adrenoreceptor in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of rat lung paraffin embedded sections using Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:100). α2B-Adrenoreceptor is expressed in the respiratory epithelium of the bronchioli (arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of α2B-Adrenoreceptor in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of rat lung paraffin embedded sections using Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:100). α2B-Adrenoreceptor is expressed in the respiratory epithelium of the bronchioli (arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain. Expression of α2B-Adrenergic Receptor in mouse cerebellar nuclei.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. α2B-Adrenergic Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appears in neuronal profiles. B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR021), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of α2B-Adrenergic Receptor in mouse cerebellar nuclei.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. α2B-Adrenergic Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appears in neuronal profiles. B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR021), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Expression of α2B-Adrenergic Receptor in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. α2B-Adrenergic Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appears in Purkinje cells (arrows) and in the molecular layer (M). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR021), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). M = molecular layer, G = granule layer.
Expression of α2B-Adrenergic Receptor in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. α2B-Adrenergic Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appears in Purkinje cells (arrows) and in the molecular layer (M). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR021), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). M = molecular layer, G = granule layer.
- IUPHAR RECEPTOR DATABASE | ADRENOCEPTORS
- Piascik, M.T. and Perez, D.M. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298, 403.
- Link, R.E. et al. (1996) Science 273, 803.
- Makaritsis, K.P. et al. (1999) Hypertension 33, 14.
- Eason, M.G. and Liggett, S.B. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25473.
- Pitcher, J.A. et al. (1998) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 653.
- Kurose, H. and Lefkowitz, R.J. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10093.
Adrenergic receptors (also called adrenoceptors) are the receptors for the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline (called epinephrine and norepinephrine in the United States). Adrenaline and noradrenaline play important roles in the control of blood pressure, myocardial contractile rate and force, airway reactivity, and a variety of metabolic and central nervous system functions.
Adrenergic receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily of membrane proteins. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, and a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus.
Adrenoceptors are divided into three types: α1, α2 and β-adrenoceptors. Each type is further divided into at least three subtypes: α1A, α1B, α1D, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2, β31,2. Adrenoceptors are expressed in nearly all peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system1,2.
The α2B-adrenoceptor has a distinct pattern of expression within the brain, liver lung and kidney, and recent studies using the knock out mouse system have shown that disruption of this receptor indeed affects mouse viability3, blood pressure responses to α2-adrenoceptor agonists3 and the hypertensive response to salt loading4.
Like the α2A-adrenoceptor subtype, the α2B-adrenoceptor undergoes short term agonist promoted desensitization5. This desensitization is due to the phosphorylation of the receptor by G-protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs)6 which ultimately promotes uncoupling of the receptor from the G-protein subunit7.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat α2B-adrenoceptor. Anti-α2B-Adrenergic Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AAR-021) can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize α2B-adrenoceptor from mouse, rat, and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse sample:
Hamlett, E.D. et al. (2020) Neurobiol. Dis. 134, 104616.

