Overview
- Peptide (C)KMSEQ STISEHILQK, corresponding to amino acid residues 6-20 of rat 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (Accession P30994). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain, rat uterus, mouse brain and human brain neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) lysates (1:200-1:1000).
 Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 5), rat brain (lanes 2 and 6), rat uterus (lanes 3 and 7) and human SH-SY5Y brain neuroblastoma cell (lanes 4 and 8) lysates:1-4. Anti-5HT2B Receptor (HTR2B) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-035), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 5), rat brain (lanes 2 and 6), rat uterus (lanes 3 and 7) and human SH-SY5Y brain neuroblastoma cell (lanes 4 and 8) lysates:1-4. Anti-5HT2B Receptor (HTR2B) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-035), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-5HT2B Receptor (HTR2B) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with 5HT2B Receptor/HTR2B (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SR035).
- Mouse brain sections (1:400).
5-HT is involved in a variety of physiological and biological processes. In the brain, 5-HT has been found to affect sleep, mood, appetite, anxiety, aggression, perception, pain, and cognition1. Signaling of 5-HT is mediated by receptors that are located on the cell membrane of neurons and most other cells in the body. The 5-HT2 family consists of three G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs): 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C2. Like other members, they are transmembrane proteins consisting of seven membrane-spanning α-helical segments with an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus. The binding of 5-HT to one of its receptors is thought to elicit a conformational change that activates associated heterotrimeric G proteins and recruits other downstream signaling/scaffolding molecules, such as GPCR kinases and β-arrestins.
5-HT2B receptors have been found to be present in both rodent and human tissues, particularly in the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, bone, and central nervous system2. Only low expression levels are found in the brain and blood. The highest expression levels are found in the stomach fundus3.
Over-expression of 5-HT2B receptors in hearts of transgenic mice results in cardiac hypertrophy and decreased ventricular function due to enhanced extracellular matrix (ECM) and remodeling. Likewise, genetic deletion of 5-HT2B receptors was shown to lead to ventricular dilation and incomplete cardiac development5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
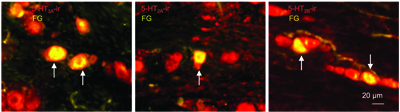
Expression of metabotropic and ionotropic 5-HT Receptors in mouse trigeminal ganglion.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse trigeminal ganglion (TG) sections using Alomone Labs Anti-5HT2A Receptor (HTR2A) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-033), Anti-5HT2B Receptor (HTR2B) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-035) and Anti-5HT3A Receptor (HTR3A) Antibody (#ASR-031) (red) shows that all three receptors are expressed in retrogradely labeled whisker afferent neurons.Adapted from Chang, W. et al. (2016) with permission of the National Academy of Sciences, USA.
