Overview
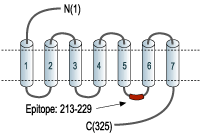
- Peptide (C)KKVSASSGDPQKYYGKE, corresponding to amino acid residues 213-229 of human A1AR (Accession P30542). 3rd intracellular loop.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1, 3) and rat kidney (lanes 2, 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1, 3) and rat kidney (lanes 2, 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Adenosine A1 Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR006).
 Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat cortexImmunohistochemical staining of rat cortex frozen section using Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006). A. A1AR (green) appears in neurons (triangles) and in astrocytes (arrows). B. Parvalbumin staining (red) appears in cortical interneurons. C. Confocal merge of images demonstrates the existence of A1AR in a subset of cortical interneurons and astrocytes.
Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat cortexImmunohistochemical staining of rat cortex frozen section using Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006). A. A1AR (green) appears in neurons (triangles) and in astrocytes (arrows). B. Parvalbumin staining (red) appears in cortical interneurons. C. Confocal merge of images demonstrates the existence of A1AR in a subset of cortical interneurons and astrocytes. Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat medial septumImmunohistochemical staining of rat medial septum frozen section using Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006). A. A1AR (green) appears in neurons (right pointing triangles). B. Parvalbumin staining (red) appears in medial septal neurons. C. Confocal merge of demonstrates expression of A1AR in a subset of medial septal neurons.
Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat medial septumImmunohistochemical staining of rat medial septum frozen section using Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006). A. A1AR (green) appears in neurons (right pointing triangles). B. Parvalbumin staining (red) appears in medial septal neurons. C. Confocal merge of demonstrates expression of A1AR in a subset of medial septal neurons.
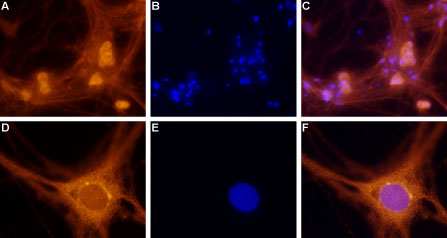 Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat DRG primary cultureImmunocytochemical staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) primary culture.
Expression of Adenosine A1 Receptor in rat DRG primary cultureImmunocytochemical staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) primary culture.
A. Staining of DRG cells with Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006) (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit AlexaFluor-555 secondary antibody.
B. Nuclear staining of cells using the cell-permeable dye Hoechst 33342.
C. Merged images of A and B.
F. Merged images of D and E.
Magnification:
A-C: x20
D-F: x100
- Okusa, M.D. (2002) Am. J. Physiol. 282, F10.
- Nakata, H. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 16545.
- Linden, J. (1991) FASEB J. 5, 2668.
- Park, K.S. et al. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 299, 501.
- Rice, A.M. et al. (2000) Endocrinology 141, 1442.
- LaNoue, K.F. and Martin, L.F. (1994) FASEB J. 8, 72.
- Synowitz, M. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 8550.
- Lelievre, V. et al. (1998) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 341, 289.
- Khoo, H.E. et al. (1996) Cancer Lett. 106, 17.
Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside generated locally in tissues under conditions of hypoxia, ischemia, or inflammation. It modulates a variety of physiological functions in many tissues including the brain and heart.1,2 Adenosine exerts its actions via four specific adenosine receptors (also named P1 purinergic receptors): Adenosine A1 Receptor (A1AR), Adenosine A2A Receptor (A2AAR), Adenosine A2B Receptor (A2BAR), and Adenosine A3 Receptor (A3AR). All are integral membrane proteins and are members of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, a cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus, and a third intracellular loop that is important for binding G proteins.1-3 The adenosine receptors can be distinguished on the basis of their differential selectivity for adenosine analogs.1-3
A1AR is widely distributed and has been well characterized. High expression of A1AR is found in the brain (mainly in the cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampus), dorsal horn of the spinal cord, adrenal gland, and atria, and to a lower extent in several other tissues including adipose tissue, the colon, and kidney.2,4
A1AR modulates the activity of several ion channels. Activation of A1AR (by adenosine, its major agonist) inhibits N-type Ca2+ channels via a voltage-dependent, pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive pathway in neurons of the rat major pelvic ganglia (MPG).5
Since A1AR is the most prominent adenosine receptor in adipocytes, it has become a natural target for research on obesity, which is a major health problem.6,7 A possible role in cell proliferation and carcinogenesis has also been suggested for A1AR.8-10
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to introduce a new antibody directed against human adenosine A1 receptor. Anti-Adenosine A1 Receptor Antibody (#AAR-006) can be used in western blot analysis, immunocytochemical and immunohistochemical applications. It has been designed to recognize adenosine A1R from rat, mouse and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Western blot of human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line (hCMEC)/D3. Tested in cell lines with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated ADORA1 knockout.
Zhao, Z. et al. (2020) Virulence. 11, 980.
- Human ovarian cancer A1780 and HEY cell lysates.
Sureechatchaiyan, P. et al. (2018) Purinergic Signal. 14, 395. - Rat retina cell lysate (1:500).
Vindeirinho, J. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e67499. - Mouse muscle, brain and spinal cord lysates (1:5000).
Garcia, N. et al. (2013) Eur. J. Neurosci. 38, 2229.
- Mouse cochlea sections.
Lin, S.C.Y. et al. (2019) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13, 207. - Mouse plastic-embedded muscle sections (1:100).
Garcia, N. et al. (2013) Eur. J. Neurosci. 38, 2229.
