Overview
- Peptide (C)RQLKQMESQPLPGER, corresponding to amino acid residues 201-215 of mouse adenosine A2A receptor (Accession Q60613). 3rd intracellular loop.

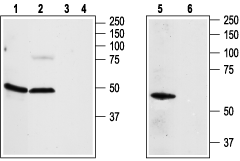 Western blot analysis of rat aortic endothelial cells (lanes 1, 3), rat brain (lanes 2, 4) and Jurkat (lanes 5, 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat aortic endothelial cells (lanes 1, 3), rat brain (lanes 2, 4) and Jurkat (lanes 5, 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002), (1:200).
3,4,6. Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Adenosine A2A Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR002).
 Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptor in mouse diagonal bandImmunohistochemical staining of mouse diagonal band using Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002). A2aR (green) appears in the broca of individual neurons (arrows) and in neuropil (asterisk). DAPI is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptor in mouse diagonal bandImmunohistochemical staining of mouse diagonal band using Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002). A2aR (green) appears in the broca of individual neurons (arrows) and in neuropil (asterisk). DAPI is used as the counterstain.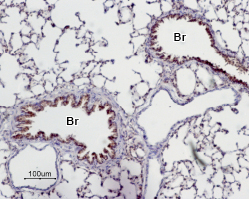 Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptor in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin emedded rat lung sections using Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002), (1:50). A2aR is expressed in the respiratory epithelium of the bronchioli (Br). Note that smooth muscle and endothelium in blood vessels are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptor in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin emedded rat lung sections using Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002), (1:50). A2aR is expressed in the respiratory epithelium of the bronchioli (Br). Note that smooth muscle and endothelium in blood vessels are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
- Rat neurospheres (Benito-Munoz, M. et al. (2016) Glia 64, 1465.).
- Okusa, M.D. (2002) Am. J. Physiol. 282, F10.
- Fredholm, B.B. et al. (2001) Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 527.
- Nakata, H. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 16545.
- Cunha, R.A. (2001) Neurochem. Int. 38, 107.
- Fredholm, B.B. et al. (2000) Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 362, 364.
- Canals, M. et al. (2005) J. Neurochem. 92, 337.
- Ohta, A. and Sitkovsky, M. (2001) Nature 414, 916.
- Ohta, A. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103, 13132.
Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside generated locally in tissues under conditions of hypoxia, ischemia, or inflammation. It modulates a variety of physiological functions in many tissues including the brain and heart.1,2 Adenosine exerts its actions via four specific adenosine receptors (also named P1 purinergic receptors): Adenosine A1 Receptor (A1AR), Adenosine A2A Receptor (A2AAR), Adenosine A2B Receptor (A2BAR), and Adenosine A3 Receptor (A3AR). All are integral membrane proteins and are members of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. They share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular -NH2 terminus, cytoplasmic -COOH terminus, and a third intracellular loop important for binding G proteins.1-3 The adenosine receptors can be distinguished on the basis of their differential selectivity for adenosine analogs.1-3
Adenosine receptors control neurotransmitter release through the facilitatory A2AAR and the inhibitory A1AR.4 A2AAR and A1AR are the major adenosine receptor subtypes expressed in the central nervous system (CNS). A2AAR is mainly expressed in the striatum on GABAergic striatopallidal neurons, while A1AR is widely distributed throughout the CNS.5,6
A2AAR was suggested to play a critical role in attenuation of systemic inflammatory responses and prevention of extensive tissue damage.7 It was suggested that extracellular adenosine that accumulates in inflamed and damaged tissue may activate the A2AAR expressed in immune cells leading to termination/inhibition of the immune response.7 It was further suggested that this same mechanism may protect tumors from antitumor T cells through an immunosuppressive signal generated by the activation of A2AAR on T cells by extracellular adenosine produced from hypoxic cancerous tissues.8
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Adenosine A2A Receptor Antibody (#AAR-002) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize A2aR from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Western blot of mouse N2a cells. Tested in cell lines treated with AAV-shA2AR.
Gomez-Castro, F. et al. (2021) Science. 374, 6568.
- Human ovarian cancer A1780 and HEY cell lysates.
Sureechatchaiyan, P. et al. (2018) Purinergic Signal. 14, 395. - Human skin lysate.
Andres, R.M. et al. (2017) J. Invest. Dermatol. 137, 123. - Rat lung lysate.
Densmore, J.C. et al. (2017) Exp. Lung Res. 43, 38. - Mouse brain lysate.
Ingwersen, J. et al. (2016) J. Neuroinflammation 13, 1.
- Rat Cochlea sections (1:50).
Han, B.R.X. et al. (2019) Cells 8, 877.
- Rat neurospheres.
Benito-Munoz, M. et al. (2016) Glia 64, 1465.
