Overview
|
| Bioz Stars Product Rating | |
| The world's only objective ratings for scientific research products | |
| Mentions | |
| Recency | |
| View product page > | |
Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-120) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope and can potentially be used for detecting the protein in living cells. It has been designed to recognize ADAM22 from rat, mouse, and human samples.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Applications
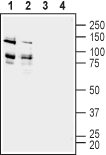 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-120), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-120), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with ADAM22 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR120).
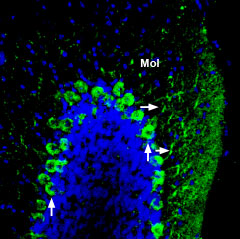 Expression of ADAM22 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-120), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody. ADAM22 staining (green) appears in Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) and in dendrites (horizontal arrows) in the molecular layer (Mol). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of ADAM22 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-ADAM22 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-120), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody. ADAM22 staining (green) appears in Purkinje cells (vertical arrows) and in dendrites (horizontal arrows) in the molecular layer (Mol). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Citations (1)
Specifications
- Peptide (C)HNDDAKTGITLSGNG, corresponding to amino acid residues 715-729 of mouse ADAM22 (Accession Q9R1V6). Extracellular, N-terminus.

Scientific Background
ADAMs (a disintegrin and metalloproteinases) are multi-domain transmembrane glycoproteins with diverse roles in physiology and disease. Notably, 8 of 21 ADAMs lack functional metalloproteinase domains and are implicated in protein-protein interactions instead of membrane protein ectodomain shedding.
ADAM22 is a non-proteinase which acts as a post synaptic receptor for the secreted neurotransmission modulator LGI-1 at neural synapses. ADAM22 is a compact four-leaf clover with the metalloproteinase-like domain (Domain M) held in the concave face of a rigid module formed by the disintegrin (Domain D), cysteine-rich (Domain C), and epidermal growth factor-like domains (Domain E). The largest domain in the four-leaf clover, domain M, is distal to the cell membrane. Following domain M, domain D and domain C zigzag to domain E in a compact, but not extended fashion. A 15-amino acid linker, leads the C terminus of domain E to the membrane. The loss of metalloproteinase activity is ensured by the absence of critical catalytic residues, the filling of the substrate groove, and the steric hindrance by the cysteine-rich domain. The extracellular domain of ADAM22 interacts with LGI-1, whereas its cytoplasmic PDZ-binding motif recruits PSD-95. The link of ADAM22 and LGI-1 to AMPA receptors establishes their roles in glutamate neurotransmission1.
Mutations that impair LGI-1 binding to ADAM22 are implicated in the pathogenesis of Autosomal dominant lateral temporal epilepsy (ADTLE), a focal epilepsy syndrome characterized by focal seizures with prominent auditory or aphasic symptoms, normal magnetic resonance imaging, and usually benign evolution2.
