Overview
- Peptide (C)KIRKNTWASHSSK, corresponding to amino acid residues 212-224 of the rat Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas receptor (Accession P12526). 3rd intracellular loop.

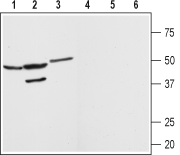 Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4) kidney (lanes 2 and 5) and heart (lanes 3 and 6) membranes:1-3. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4) kidney (lanes 2 and 5) and heart (lanes 3 and 6) membranes:1-3. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR013). Western blot analysis of mouse kidney membranes:1. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse kidney membranes:1. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013), (1:200).
2. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR013). Western blot analysis of human HeLa cervix adenocarcinoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013),(1:200).
Western blot analysis of human HeLa cervix adenocarcinoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (AAR-013),(1:200).
2. Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-AR013).
 Expression of Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of rat kidney paraffin embedded sections using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013), (1:100). Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas receptor (brown staining) is detected in proximal tubules (PT) and distal tubules (DT) in the renal cortex. Collecting ducts (CD) are less stained and both glomeruli (G) and blood vessels (A) are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor in rat kidneyImmunohistochemical staining of rat kidney paraffin embedded sections using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013), (1:100). Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas receptor (brown staining) is detected in proximal tubules (PT) and distal tubules (DT) in the renal cortex. Collecting ducts (CD) are less stained and both glomeruli (G) and blood vessels (A) are negative. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
- Mouse microglia culture (1:20) (Foulquier, S. et al. (2019) Angiogenesis 22, 481.).
- Santos, R.A. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 8258.
- Alenina, N. et al. (2008) Exp. Physiol. 93, 528.
- Santos, R.A. et al. (2008) Exp. Physiol. 93, 519.
The Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas receptor is the recently identified receptor of the biologically active heptapeptide Angiotensin-(1-7).1
Angiotensin (Ang)-(1-7) is a metabolite of the well known peptide hormone Angiotensin (Ang) II, a key component of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) that has a central role in cardiovascular homeostasis.
Considerably interest in Ang-(1-7) and its receptor aroused in the last few years since it became apparent that it can counterbalance most of Ang II effects. Thus Ang-(1-7) has vasodilator and hypotensive effects as well as antiarrhythmic and cardioprotective roles.2, 3
The Ang-(1-7) Mas receptor belongs to the 7-transmembrane domain, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily and was originally described as a protooncogene.
Signaling via the Ang-(1-7) Mas receptor is still poorly elucidated however, evidence indicates that the receptor is coupled to a Gq/11 protein that activates phospholipase C (PLC).2,3
The Ang-(1-7) Mas receptor is expressed in several organs including heart, kidney, blood vessels, testis and brain. Studies with Ang-(1-7) Mas receptor knockout mice have demonstrated the key role of this receptor in cardiovascular regulation as well as in the regulation of learning and memory.2
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013) is a highly specific antibody designed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Ang-(1-7) Mas receptor from rat, mouse, and human samples.
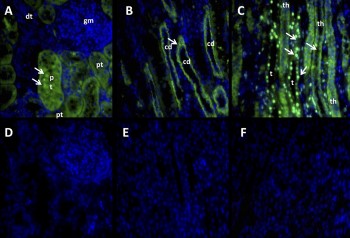
Expression of Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor in sheep kidney.Immunohistochemical staining of sheep kidney sections using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013). A. Mas receptor staining in the cortex (green) is mostly associated with the proximal tubules and is absent in in the glomerulus. B. Mas receptor staining is observed in the collecting ducts in the medullary region. C. The limb of Henle also shows Mas receptor staining. D-F. Mas receptor staining is abolished when the antibody is pre-incubated with the control peptide antigen.Adapted from Gwathmey, T.M. et al. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 299, F983. with permission of The American Physiological Society.
Applications
Citations
 Expression of Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor in mouse heart and kidney.A, C. Immunohistochemical staining of mouse over-expressing growth hormone (GH) using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013). Mas receptor staining decreases in mice over-expressing GH (right panels). B, D. Western blot analysis of same tissues in A and C using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody also shows a decrease in Mas receptor’s expression.
Expression of Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor in mouse heart and kidney.A, C. Immunohistochemical staining of mouse over-expressing growth hormone (GH) using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody (#AAR-013). Mas receptor staining decreases in mice over-expressing GH (right panels). B, D. Western blot analysis of same tissues in A and C using Anti-Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptor Antibody also shows a decrease in Mas receptor’s expression.
Adapted from Munoz, M.C. et al. (2014) with permission of the Society for Endocrinology.
- Mouse brain sections. Tested in MAS-/- mice.
Freund, T. et al. (2012) Cell Tissue Res. 348, 29.
- Mouse brain and macrophage lysate (1:250).
Hammer, A. et al. (2016) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 14109. - Mouse brain lysate (1:2000).
Uekawa, K. et al. (2016) J. Alzheimers Dis. 53, 127. - Mouse kidney lysate.
Ali, Q. et al. (2016) J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 17, 3. - Sheep kidney lysate (1:250).
Wilson, B.A. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, F637. - Rat carotid arteries lysate (1:500).
Olivon, V.C. et al. (2015) Peptides 71, 250. - Rat heart lysates.
Hao, P.P. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 308, H1007. - Rat kidney lysate.
Zimmerman, M.A. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 306, F1136. - Mouse kidney lysate (1:4000).
Munoz, M.C. et al. (2014) J. Endocrinol. 221, 215. - Mouse skeletal muscle lysate (1:7500).
Sabharawal, R. et al. (2014) Clin. Sci. 127, 101. - Rat brain lysate (1:2000).
Du, D. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e70976. - Mouse penis lysate (1:200).
Fraga Silva, R.A. et al. (2013) J. Sex. Med. 10, 2430. - Rat heart lysate (1:5000).
Wang, H. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, 76992. - Mouse lung lysate (1:500).
Rodrigues-Machado, M.G. et al. (2013) Br. J. Pharmacol. 170, 835. - Sheep brain medulla lysate (1:250).
Marshall, A.C. et al. (2013) Peptides 44, 25.
- Rat carotid sections (1:300).
Olivon, V.C. et al. (2015) Peptides 71, 250. - Mouse uterine artery and placenta sections (1:400).
Yamaleyeva, L.M. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 309, E84. - Mouse kidney sections (1:100).
Munoz, M.C. et al. (2014) J. Endocrinol. 221, 215. - Mouse skeletal muscle sections (1:200).
Sabharawal, R. et al. (2014) Clin. Sci. 127, 101. - Rat brain sections.
Freund, M. et al. (2014) Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 24, 302. - Rat striatum.
Regenhardt, R.W. et al. (2014) Exp. Physiol. 99, 442. - Mouse brain sections. Tested in MAS-/- mice.
Freund, T. et al. (2012) Cell Tissue Res. 348, 29. - Sheep kidney sections.
Gwathmey, T.M. et al. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 299, F983.
- Mouse microglia culture (1:20).
Foulquier, S. et al. (2019) Angiogenesis 22, 481.
- Mouse microglia culture (1:20).
Foulquier, S. et al. (2019) Angiogenesis 22, 481. - Mouse brain sections. Tested in MAS-/- mice.
Freund, T. et al. (2012) Cell Tissue Res. 348, 29.
- Freund, M. et al. (2012) Cell Tissue Res. 348, 29.
- Lakshmanan, A.P. et al. (2012) Biochem. Pharmacol. 83, 653.
- Muñoz, M.C. et al. (2012) Regul. Pept. 177, 1.
- Oh, Y.B. et al. (2012) Peptides. 37, 79.
- Sukumaran, V. et al. (2012) Life Sci. 90, 289.
- Silva, D.M. et al. (2011) J. Appl. Physiol. 111, 1272.
- Sukumaran, V. et al. (2011) Int. J. Biol. Sci. 7, 1077.
- Yang, R.F. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. 300, C58.
- Ferreira, A.J. et al. (2010) Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 4, 83.
- Gwathmey, T.M. et al. (2010) Hypertension 55, 166.
- Varagic, J. et al. (2010) Am. J. Nephrol. 32, 557.
