Overview
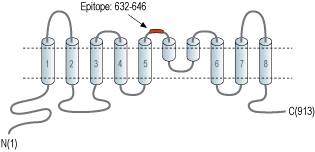
- Peptide (C)HSKRPEQWDLDHSLE, corresponding to amino acid residues 632-646 of mouse Anoctamin-2 (Accession Q8CFW1). 3rd extracellular loop.
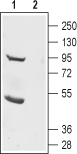 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACL-012), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACL-012), (1:200).
2. Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with TMEM16B/ANO2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CL012).
 Expression of Anoctamin-2 in mouse olfactory bulbImmunohistochemical staining of mouse olfactory bulb using Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACL-012), (1:200). A. Anoctamin-2 is detected in anoctamin-positive axons (arrows). B. Staining with mouse anti-synaptophysin (red) and DAPI (blue) reveals the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb (asterisk). C. Merge of the above images reveals the spatial relationship of the anotctamin-2 positive axons to the olfactory bulb organization.
Expression of Anoctamin-2 in mouse olfactory bulbImmunohistochemical staining of mouse olfactory bulb using Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACL-012), (1:200). A. Anoctamin-2 is detected in anoctamin-positive axons (arrows). B. Staining with mouse anti-synaptophysin (red) and DAPI (blue) reveals the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb (asterisk). C. Merge of the above images reveals the spatial relationship of the anotctamin-2 positive axons to the olfactory bulb organization.
- Rat olfactory sensory neurons, (Mura, C.V. et al. (2017) BMC Neurosci. 18, 61.).
- Hartzell, H.C. et al. (2009) J. Physiol. 587, 2127.
- Sheridan, J.T. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 1381.
- Caputo, A. et al. (2008) Science 322, 590.
- Yang, Y.D. et al. (2008) Nature 455, 1210.
- Schroeder. B.C. et al. (2008) Cell 134, 1019.
- Rock, J.R. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 14875.
- Rock, J.R. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 321, 141.
- Stephan, A.B. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 11776.
- Hengl, T. et al. (2010) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 6052.
- West, R.B. et al. (2004) Am. J. Pathol. 165, 107.
- Espinosa, I. et al. (2008) Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 32, 210.
- Huang, X. et al. (2006) Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45, 1058.
- Carles, A. et al. (2006) Oncogene 25, 1821.
Anoctamin (ANO or TMEM16) is a family of 10 membrane proteins. This family is named so because these channels are selective to ANions and have eight (OCT) transmembrane domains. Also, these channels are subject to glycosylation in their extracellular loops and have both intracellular N- and C-termini1. Members of this family are expressed in a broad range of different organisms ranging from mammals, flies, worms, plants and yeast1. Alternative splicing is known to affect these channels and regarding their oligomerization state, homedimerization has been observed although when heterologously expressed, these channels may hetero oligomerize2.
Ano1 (or TMEM16A, DOG1 and others) the first member to be identified was found to be a Ca2+-activated Cl- channel3-5 therefore other members are likely to also be Cl- channels. These channels are expressed in many different tissues: bronchiolar epithelial cells, pancreatic acinar cells, proximal kidney tubule epithelium, retina, dorsal root ganglia and submandibular gland1. In fact, Ano1 gained a lot of attention as its activation may serve as a therapeutic treatment for cystic fibrosis since it is also expressed in the airways6. These Ca2+-activated Cl- channels are believed to play a role in development as knockout of Ano1 in mice causes abnormal development of the trachea7. Ano2 (TMEM16B) has been shown to mediate Ca2+-activated Cl- current in olfactory epithelium and photoreceptor synapses2,8,9.
Although relatively newly discovered channels, they are being discovered in many medical indications. Ano1 has become a marker in gastrointestinal tumors as its expression is significantly upregulated10,11. Similarly, Ano1 is also highly expressed in other carcinomas12,13.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-TMEM16B (ANO2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACL-012) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of mouse Anoctamin-2. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Anoctamin-2 from mouse, rat, and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate. Tested in Ano2-/- mice
Zhang, W. et al. (2015) PLoS ONE 10, e0142160.
- Mouse primary RPE cells (1:500).
Keckeis, S. et al. (2017) Exp. Eye Res. 154, 139. - Mouse brain lysate (also tested in Ano2-/- mice).
Zhang, W. et al. (2015) PLoS ONE 10, e0142160.
- Mouse tongue sections.
Cherkashin, A.P. et al. (2016) Pflugers Arch. 468, 305.
- Rat olfactory sensory neurons.
Mura, C.V. et al. (2017) BMC Neurosci. 18, 61.
