Overview
- Peptide (C)DHREERKKTIELTAH corresponding to amino acid residues 251-265 of rat AQP5 (Accession number P47864). Intracellular, C-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of mouse salivary gland (1 and 3) and rat lung (2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse salivary gland (1 and 3) and rat lung (2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody, preincubated with Aquaporin 5 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-QP005).- Human primary lung epithelial cells (Marconett, C.N. et al. (2013) PLoS Genet. 9, e1003513.).
 Expression of AQP5 in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of rat lung sections using Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005), (left panel). The strong staining in the alveoli (red brown) is consistent with type 1 pneumocytes (arrows). Counterstain of cell nuclei appears blue. A negative control is shown in the right panel.
Expression of AQP5 in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of rat lung sections using Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005), (left panel). The strong staining in the alveoli (red brown) is consistent with type 1 pneumocytes (arrows). Counterstain of cell nuclei appears blue. A negative control is shown in the right panel.
- Mouse submandibular salivary cells (1:400) (Joo, E.E. et al. (2016) J. Dent. Res. 95, 1518.).
- Agre, P. et al. (2002) J. Physiol. 542.1, 3.
- Towne, J.E. et al. (2000) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 22, 34.
- Yang, F. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 32173.
The importance of the aquaporin water channels was underscored by awarding the 2003 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Peter Agre “for the discovery of water channels”. Today, eleven mammalian proteins that belong to the aquaporin family have been identified. The proteins present a conserved structure of six transmembrane domains with intracellular N- and C-termini.
Aquaporin 5 (AQP5) is expressed in secretory glands, lung and eye, where it works in modulating the rate of fluid release. Since a number of pathological conditions including pulmonary edema, respiratory distress syndrome and congestive heart failure are characterized by disrupted fluid transport, it has been suggested that modulation of the expression of AQP5 could be a novel modality of treatment of the above illnesses. Indeed, several studies have shown that AQP5 expression is downregulated in animal models of acute lung infection.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize AQP5 from mouse, rat, and human samples.
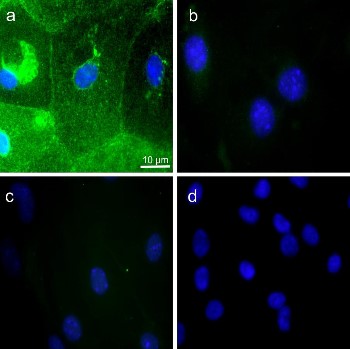
Expression of Aquaporin 5 in mouse ATI-like cells.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse ATI-like cells isolated from lungs using Anti-Aquaporin 5 Antibody (#AQP-005). a. AQP5 staining (green). b. AQP5 staining is abolished when antibody is preincubated with the control antigen. c. Cells incubated with a matching isotype control. d. A negative control using mouse endothelial cells.Adapted from Barnthaler, T. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7, 7923. with permission of Nature publishing group.
Applications
Citations
- Rat AT2 cell lysate.
Liebler, J.M. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, L114. - Human primary lung epithelial cells.
Marconett, C.N. et al. (2013) PLoS Genet. 9, e1003513.
- Mouse submandibular glands (1:400).
Joo, E.E. et al. (2016) J. Dent. Res. 95, 1518. - Mouse submandibular salivary glands.
Gervais, E.M. et al. (2015) Anat. Rec. 298, 1622. - Rat duodenum.
Collaco, A.M. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 305, G258.
- Mouse ATI-like cells.
Barnthaler, T. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7, 7923. - Mouse submandibular salivary cells (1:400).
Joo, E.E. et al. (2016) J. Dent. Res. 95, 1518.
- Hollborn, M. et al. (2011) Curr. Eye Res. 36, 850.
- Demaio, L. et al. (2009) Am. J. Physiol. 296, L1051.
- Yamazaki, D. et al. (2009) Development 136, 2355.
- Nagai, K. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 354, 579.
- Takayasu, H. et al. (2007) J. Ped. Surg. 42, 415.
