Overview
- Peptide (C)EKDGAKKSLMQRLALK, corresponding to amino acid residues 4-19 of rat AQP9 (Accession P56627). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain, testis and liver membranes (1:200). Rat H4-BB-E-C3 hepatoma cell line lysate (1:200). Mouse brain membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4), testis (lanes 2 and 5) and liver (lanes 3 and 6) membranes:1,2,3. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4), testis (lanes 2 and 5) and liver (lanes 3 and 6) membranes:1,2,3. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
4,5,6. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody, preincubated with Aquaporin 9 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-QP009).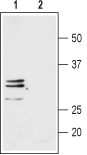 Western blot analysis of rat H4-II-E-C3 hepatoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat H4-II-E-C3 hepatoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
2. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody, preincubated with Aquaporin 9 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-QP009). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody (#AQP-009), (1:200).
2. Anti-Aquaporin 9 Antibody, preincubated with Aquaporin 9 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-QP009).
- Rat liver and testis sections (paraffin embedded), (1:100).
Aquaporin 9 (AQP-9) belongs to a family of membrane proteins that allow passage of water and certain other solutes through biological membranes.1 The family is composed of 13 members (AQP-0 to AQP-12). Little is known about the function of the two newest members, AQP-11 and AQP-12.
The aquaporins can be divided into two functional groups based on their permability characteristics: the aquaporins that are permeated primarily by water (AQP-1, AQP-2, AQP4, AQP-5, AQP-6, AQP-8), and the aquaglyceroporins that are permeated by water and other small solutes such as glycerol. This last group includes AQP-3, AQP-7, AQP-9 and AQP-10.
The proteins present a conserved structure of six transmembrane domains with intracellular N- and C-termini. The functional channel is a tetramer but each subunit has a separate pore and therefore the functional channel unit contains four pores.2
AQP-9 is expressed in several tissues including the brain, liver, testis and spleen. In the liver AQP-9 has a central role in glycerol metabolism as demonstrated in experiments using AQP-9 knockout mice: mice deficient in AQP-9 expression showed enhanced plasma levels of glycerol and triglycerides.3
