Overview
- Peptide KPRSGLEEAQRRQAS(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 2-16 of rat ASIC3 (Accession O35240). Intracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysate:1. Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysate:1. Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018), (1:200).
2. Anti-ASIC3 Antibody, preincubated with ASIC3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC018).
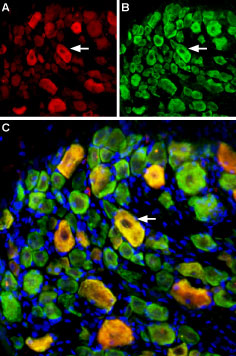 Multiplex staining of ASIC1 and ASIC3 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) sections using Guinea pig Anti-ASIC1 Antibody (#ASC-014-GP), (1:400) and rabbit Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018), (1:400). A. ASIC3 staining. B. ASIC1 staining in same section (green). C. Merge of the two images shows some co-localization (arrow). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of ASIC1 and ASIC3 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) sections using Guinea pig Anti-ASIC1 Antibody (#ASC-014-GP), (1:400) and rabbit Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018), (1:400). A. ASIC3 staining. B. ASIC1 staining in same section (green). C. Merge of the two images shows some co-localization (arrow). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).- Rat trigeminal ganglia (1:400) (Yan, J. et al. (2013) Headache 53, 1250.).
- Human SH-SY5Y cells (Xiong, Q.J. et al. (2012) Am. J. Physiol. 303, C376.)
- Kellenberger, S. and Schild, L. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 735.
- Chen, C.C. et al. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 8992.
- Price, M.P. et al. (2001) Neuron 32, 1071.
ASIC3 is a member of a family of Na+ channels that are activated by external protons. The family includes four additional members: ASIC1, ASIC2, ASIC4 and ASIC5. The ASICs are in fact part of a larger superfamily named degenerin/epithelial Na+ channels (DEG/ENaC) and share with it the same basic characteristics: two transmembrane spanning domains, a large extracellular domain and short intracellular N- and C-termini.
The functional channel is composed of 4 subunits that can be assembled as homo- or heterotetramers with the other ASIC subunits.
A drop in external pH opens the channel resulting in an inward cation current that is quickly inactivated even in the continuous presence of protons in the medium, although a small residual current may persist.
Several lines of evidence indicate that ASIC3 may function as a pain sensor. First, it is specifically located in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons and in nociceptors that are involved in pain detection and transmission. In addition, in conditions such as inflammation and cardiac ischemia that include tissue acidosis and thus pain, ASIC3 currents have been detected. Finally, ASIC3 deficient mice display altered sensitivity to high intensity pain produced by heat or acid.
Interestingly, while in rats ASIC3 is expressed almost exclusively in DRG neurons, in humans its expression is more widespread suggesting a more extensive role in human nociception.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize ASIC3 from rat, human, and mouse samples.
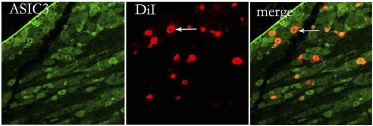
Expression of ASIC3 in rat trigeminal ganglia.Immunohistochemical staining of rat trigeminal ganglia (TG) sections using Anti-ASIC3 Antibody (#ASC-018). ASIC3 staining (green) appears in TG neurons (left panel) and coincides with FAST DiI staining (red), (right panel).Adapted from Meng, Q. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 309, C1. with permission of The American Physiological Society.
Applications
Citations
- Rat DRG lysate (1:200).
Wu, Y. et al. (2017) Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 37, 635. - Mouse bone marrow derived macrophage (BMM) lysate.
Kong, X. et al. (2013) Cell. Immunol. 281, 44. - Human SH-SY5Y cell lysate.
Xiong, Q.J. et al. (2012) Am. J. Physiol. 303, C376. - Mouse immature dentritic cells.
Tong, J. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 186, 3686.
- Rat DRG sections (1:50).
Wu, Y. et al. (2017) Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 37, 635. - Rat trigeminal sections (1:50).
Meng, Q. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 309, C1. - Rat trigeminal ganglia (1:400).
Yan, J. et al. (2013) Headache 53, 1250. - Mouse anterial synovial sections (1:500).
Kolker, S.J. et al. (2010) Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 903.
- Mouse primary DRGs (1:100).
Radu, B.M. et al. (2014) Cell Biochem. Biophys. 68, 9. - Human SH-SY5Y cell lysate.
Xiong, Q.J. et al. (2012) Am. J. Physiol. 303, C376. - Mouse dendritic cells.
Tong, J. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 186, 3686. - Mouse synoviocytes. Also tested in ASIC3-/- mice.
Kolker, S.J. et al. (2010) Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 903.
- Ohbuchi, T. et al. (2010) J. Physiol. 588, 2147.
- Akiba, Y. et al. (2008) Gut 57, 1654.
- Ye, J.H. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 355, 986.
