Overview
- Peptide CKIKFAEEDAKPKEKEAGDE, corresponding to amino acid residues 7-26 of rat ASIC4 (Accession Q9QYV9). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain, ND7/23 (mouse neuroblastoma x rat DRG neuron hybrid cell line) and dorsal root ganglion (DRG) lysate (1:200-1:500).
 Western blot analysis of mouse ND7/23 neuroblastoma x rat DRG neuron hybrid cell line (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody (#ASC-015), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse ND7/23 neuroblastoma x rat DRG neuron hybrid cell line (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody (#ASC-015), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody, preincubated with ASIC4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC015).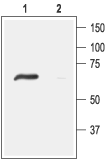 Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody (#ASC-015), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody (#ASC-015), (1:200).
2. Anti-ASIC4 Antibody, preincubated with ASIC4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC015).
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are Na+ channels activated by external protons. ASIC4 is a member of the ASIC family that includes four additional members: ASIC1, ASIC2, ASIC3 and ASIC5. The ASICs are in fact part of a larger superfamily named degenerin/epithelial Na+ channels (DEG/ENaC) and share with it the same basic characteristics: two transmembrane spanning domains, a large extracellular domain and short intracellular N- and C-termini.
The functional ASIC channel is composed of 4 subunits, which can form either a homo- or heterotetramer. The subunit composition of the tetrameric channel will determine its biophysical properties such as pH sensitivity, inactivation kinetics and channel pharmacology. In fact, the ASIC4 protein does not appear to function as a proton-gated channel when expressed alone in heterologous systems and therefore a modulatory role for this subunit has been proposed.
Expression of the ASIC4 protein has been detected in the brain, pituitary gland, spinal cord and inner ear. The functional significance of ASIC4 expression in these tissues still awaits clarification.
