Overview
- Peptide GKRFRKKSWEVYQG(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 336-349 of human B2R (Accession P30411). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012), (1:1000).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012), (1:1000).
2. Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody, preincubated with B2 Bradykinin Receptor/BDKRB2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-BR012).
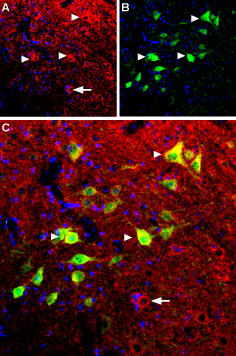 Expression of B2 bradykinin receptor in mouse spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of mouse spinal cord using Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012). A. BKR2 (red) appears in several spinal cord neurons (triangles). B. Parvalbumin (green) appears in neurons. C. Merge of BKR2 and parvalbumin shows co-expression in several neurons (triangles) but not all (arrow in C). DAPI is used as the counterstain.
Expression of B2 bradykinin receptor in mouse spinal cordImmunohistochemical staining of mouse spinal cord using Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012). A. BKR2 (red) appears in several spinal cord neurons (triangles). B. Parvalbumin (green) appears in neurons. C. Merge of BKR2 and parvalbumin shows co-expression in several neurons (triangles) but not all (arrow in C). DAPI is used as the counterstain.
- Rat trigeminal neuron primary cultures (Kawaguchi, A. et al. (2015) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 229.).
- Walker, K. et al (1995) Neurochem. Int. 26, 1.
- Böckmann, S. and Paegelow, I. (2000) J. Leukoc. Biol. 68, 587.
- Hess, J.F. et al. (2004) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 310, 488.
- Souza, D.G. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 172, 2542.
- Calixto, J.B. et al. (2000) Pain 87, 1.
Kinins are small peptides produced rapidly following tissue injury that serve as important modulators of inflammation and pain. In the periphery, the actions of kinins include vasodilatation, increased vascular permeability, stimulation of immune cells, and induction of pain. Kinins in the central nervous system (CNS) seem to initiate a similar cascade of events leading to neural tissue damage, as well as long lasting disturbances affecting blood-brain barrier function.1
Kinins, such as Bradykinin (BK), Lys-BK, desArg9-BK, and Lys-desArg9-BK, exert their action via two distinct receptors: the B1 Bradykinin receptor (BKRB1) and the B2 Bradykinin receptor (BKRB2). BKRB2 is activated by BK and Lys-BK while desArg9-BK and Lys-desArg9-BK activate BKRB1.2 Activation of BKRB2 liberates mediators of vascular tone, fibrinolysis, and pain. BKRB2, which mediates most of the physiological effects of kinins, as well as BKRB1, represent potential therapeutic targets for treatment of inflammatory disorders and cardiovascular diseases.
Both BKRB1 and BKRB2 are members of the seven-transmembrane domain, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily and share a common structure of seven putative transmembrane domains, an extracellular amino terminus, and a cytoplasmic carboxy terminus.
BKRB2 is constitutively and widely expressed throughout the CNS and peripheral nervous system and on various cell types including endothelial cells, nerve fibers, leukocytes, and mast cells.3-5
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize B2R from human, rat, and mouse samples.
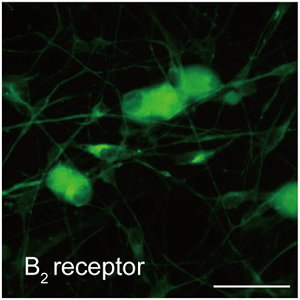
Expression of B2 bradykinin receptor in rat TG neurons.Immunocytochemical staining of rat primary trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons using Anti-B2 Bradykinin Receptor (BDKRB2) Antibody (#ABR-012). Adapted from Kawaguchi, A. et al. (2015) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 229. with permission of Frontiers.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse spinal cord.
Dutra, R.C. et al. (2013) Neurobiol. Dis. 54, 82.
- Rat brain sections (1:200).
Bitencourt, R.M. et al. (2017) Behav. Brain Res. 316, 74. - Mouse brain sections (1:200).
Bicca, M.A. et al. (2015) Behav. Brain Res. 278, 482. - Rat trigeminal neuron sections.
Kawaguchi, A. et al. (2015) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 229. - Rat lung sections.
Duehrkop, C. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e72059.
- Rat DRG culture (1:200).
Severini, C. et al. (2017) Neuropharmacology 117, 134. - Rat trigeminal neuron culture.
Kawaguchi, A. et al. (2015) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 229.
