Overview
- Peptide (C)VLEKVPVSKGQLK, corresponding to amino acid residues 166-178 of human BDNF (precursor) (Accession P23560).
- Human BDNF and mouse recombinant proBDNF (1:200).
 Western blot analysis with Anti-BDNF Antibody:1,5. Recombinant human BDNF protein (#B-250).
Western blot analysis with Anti-BDNF Antibody:1,5. Recombinant human BDNF protein (#B-250).
2,6. Recombinant mouse proBDNF protein (#B-240).
3,7. Recombinant human beta-NGF protein (#N-245).
4,8. Recombinant human Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) protein (#N-260).
Lanes 1-4: Anti-BDNF Antibody (#ANT-010), (1:200).
Lanes 5-8: Anti-BDNF Antibody, preincubated with BDNF Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT010).
Note that the antibody recognizes both BDNF and proBDNF but fails to recognize the closely related NGF and NT-3 neurotrophins.
- Mouse brain sections.
- BDNF transfected striatal cells (1:50) (del Toro, D. et al.(2006) J. Neurosci. 26, 12748.).
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors which includes nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
All neurotrophins are synthesized as preproneurotrophin precursors that are subsequently processed within the intracellular transport pathway to yield proneurotrophins that are further processed to generate the mature form. The mature form of BDNF is a non-covalent stable homodimer that can be secreted in both constitutive and regulated pathways.
BDNF conveys its activity by binding to two classes of receptors, a member of the Trk receptor tyrosine kinase family (TrkB) and the pan-neurotrophin receptor p75NTR. Binding of BDNF to the TrkB receptor triggers ligand-induced dimerization and autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues. This activates various signaling cascades such the MAPK, PI3K and PLCγ pathways that are involved in cell growth, survival and differentiation of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Interestingly, recent evidence suggests that BDNF may influence target cell function via ion channel modulation. Ion channel activity in the target cells can be modulated by a TrkB-mediated mechanism that has not yet been determined. BDNF is able to block both KV1.3 and AMPA-subtype glutamate ion channel currents in sensory neurons, while it can induce activation of the TRPC3 cation channel in neurons and of the NaV1.9 Na+ channel in hippocampal neurons. These newly recognized BDNF actions underlie its “rapid” neuronal functions that include changes in neuronal excitability, plasticity and synaptic transmission.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
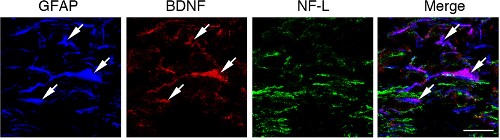
Expresssion of BDNF in mouse brain
Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-BDNF Antibody (#ANT-010). BDNF staining (purple) is expressed in astrocytes and co-localizes with GFAP (blue) but not with neurofilament-1 (NF-L), (green).Adapted from Fulmer, C.G. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 8186. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.
