Overview
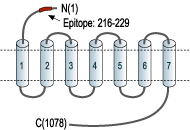
- Peptide (C)DDYGRPGIEKFREE, corresponding to amino acid residues 216-229 of human CaSR (Accession P41180). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Cell surface detection of CaSR in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of CaSR in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ACR-004-F), 2.5 µg. Cell surface detection of CaSR in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of CaSR in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ACR-004-F), 5 µg.
- Riccardi, D. and Brown, E.M. (2010) Am. J. Physiol. 298, F485.
- Hendy, G.N. et al. (2013) Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 27, 285.
The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a class C G-protein-coupled receptor encoded by a single copy gene. CaSR plays a major role in the maintenance of a physiological serum ionized Ca2+ concentration by regulating the circulating levels of parathyroid hormone1.
The N-terminus of the receptor is comprised of a signal peptide of 19 amino acids. This terminus directs the nascent CaSR polypeptide into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is then cleaved. The extracellular domain (ECD) of the mature protein has approximately 600 amino acids, comprised of a bi-lobed Venus-flytrap-like domain (VFT) connected by a cysteine-rich region and a short peptide linker to the seven transmembrane domain (TMD) with an intracellular C-terminal tail of 216 amino acids. CaSR functions as a homodimer with both covalent and noncovalent interactions between the VFT domains of each monomer. Ca2+ binds in the cleft between the two lobes of each VFT causing the lobes to close on one another and the VFT to rotate with transfer of a conformational change to the cysteine-rich region.
In the parathyroid gland, up-regulation of CaSR by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] makes the gland more responsive to extracellular Ca2+ and parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion is reduced. While somatic mutations in CASR are rare, parathyroid glands from patients with primary or severe uremic secondary hyperparathyroidism have reduced CaSR expression2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human CaSR. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, indirect flow cytometry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize CaSR from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ACR-004-F) is directly conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). This labeled antibody can be used in immunofluorescent applications such as direct flow cytometry using live cells.
