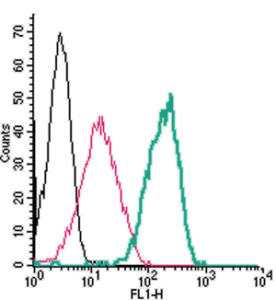Overview
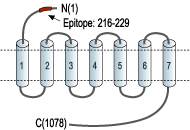
- Peptide (C)DDYG RPGIE KFREE, corresponding to amino acid residues 216-229 of human CaSR (Accession P41180). N-terminus, extracellular.
 Western blot analysis of Colo205 (lanes 1 and 3), rat liver (lanes 2 and 4) and mouse kidney (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of Colo205 (lanes 1 and 3), rat liver (lanes 2 and 4) and mouse kidney (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004), (1:200).
3,4,6. Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR004).
 Expression of CaSR in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA1 region using Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004). A. CaSR staining appears in the soma and appical dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons (arrows). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merge image of A and B pannels
Expression of CaSR in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA1 region using Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004). A. CaSR staining appears in the soma and appical dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons (arrows). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merge image of A and B pannels
 Expression of CaSR in rat C6 cellsCell surface detection of CaSR in live intact rat glioma C6 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004), (1:50), followed by Alexa-555-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit secondary antibody. B. Nuclear fluorescence staining of cells using Hoechst 33342. C. Merged images of panels A and B.
Expression of CaSR in rat C6 cellsCell surface detection of CaSR in live intact rat glioma C6 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004), (1:50), followed by Alexa-555-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit secondary antibody. B. Nuclear fluorescence staining of cells using Hoechst 33342. C. Merged images of panels A and B.
- IUPHAR RECEPTOR DATABASE.
- Racz, G.Z. et al. (2002) Gut 51, 705.
- Canaff, L. and Hendy, G.N. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 30337.
- Chen, R.A. and Goodman, W.G. (2004) Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 286, F1005
- Chattopadhyay, N. (2006) Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 290, E761.
The Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a member of subfamily C of the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. As its primary role, the CaSR is a key player in calcium homeostasis and is expressed in tissues involved in calcium metabolism such as parathyroid cells and the kidneys.1,2
The expression of CaSR was also described in other cell types and tissues, such as neurons, keratinocytes, and the pancreas. However, the role of CaSR in these cells remains to be established.1,2 Following the identification of functional vitamin D response elements in the CaSR gene, it was suggested that vitamin D might regulate the expression of CaSR.3
CaSR activation is followed by a rapid, transient increase in the cytosolic calcium concentration, resulting from mobilization of calcium from thapsigargin-sensitive intracellular stores, as well as an increased calcium influx through voltage-insensitive calcium channels located at the cell membrane.4
CaSR regulates cellular processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation under both normal and pathologic conditions.5
Recent studies demonstrated the expression in human colon epithelium of CaSR, which regulates proliferation and differentiation. In colon carcinomas, lower levels of expression were found in the cancerous tissue compared to normal colon tissue.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Calcium Sensing Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-004) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human CaSR. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, indirect flow cytometry, and immunocytochemistry, and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize CaSR from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Human Kidney sections (1:500).
Graca, J.A. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 310, F518.
- Sun, J. et al. (2013) Differentiation 85, 32.