Overview
|
| Bioz Stars Product Rating | |
| The world's only objective ratings for scientific research products | |
| Mentions | |
| Recency | |
| View product page > | |
Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat CB1 receptor. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize CB1 in human, mouse, and rat samples.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:

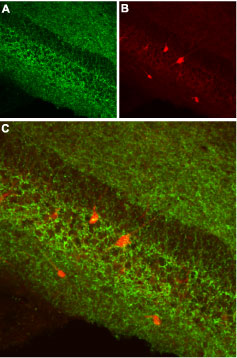
Multiplex staining of proNGF and Cannabinoid Receptor 1 in mouse hippocampal dentate gyrusImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating mouse brain frozen sections using Guinea pig Anti-proNGF Antibody (#ANT-005-GP), (1:300) and rabbit Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001), (1:300). A. proNGF staining (red) appears in the dentate gyrus (DG) granule layer (G) and in hilar interneurons (arrows). B. CB1 staining (green) appears in axonal processes surrounding the granule layer and a few hilar interneurons (arrows). C. Merge of the two images reveals co-localization of proNGF and CB1 in a few hilar cells. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Applications
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane proteins:1. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane proteins:1. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001), (1:200).
2. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR001).
- Rat cultured hippocampal neurons (1:100 for live cells, 1:500-1:100 for fixed and permeabilized cells) (McDonald, N.A. et al. (2007) Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 976.).
 Expression of CB1 receptor in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse hippocampus using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001), (1:100). A. CB1 is detected in pyramidal and infra-pyramidal layers (green). B. Staining of interneurons using mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) antibody (red). C. Confocal merge of A and B does not indicate the presence of CB1 in GABAergic cells.
Expression of CB1 receptor in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse hippocampus using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001), (1:100). A. CB1 is detected in pyramidal and infra-pyramidal layers (green). B. Staining of interneurons using mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) antibody (red). C. Confocal merge of A and B does not indicate the presence of CB1 in GABAergic cells. Expression of CB1 receptor in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampus using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001) (1:100). A. CB1 is detected in pyramidal and infra-pyramidal layers (green). B. Staining of interneurons using mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) antibody (red). C. Confocal merge of A and B does not indicate the presence of CB1 in GABAergic cells.
Expression of CB1 receptor in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampus using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-001) (1:100). A. CB1 is detected in pyramidal and infra-pyramidal layers (green). B. Staining of interneurons using mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) antibody (red). C. Confocal merge of A and B does not indicate the presence of CB1 in GABAergic cells.
Citations (25)
- HEK 293 transfected cells (1:400).
Hajkova, A. et al. (2016) Neuropharmacology 107, 201.
- Human kidney sections.
Udi, S. et al. (2010) Br. J. Pharmacol. 177, 110.
- Rat embryonic cortical neurons (1:200).
Hajkova, A. et al. (2016) Neuropharmacology 107, 201.
- Chen, S.W. et al. (2012) PloS ONE 7, e50850.
- Gonzalez Islas, C. et al. (2012) J. Neurosci. 32, 13597.
- McDonald, N.A. et al. (2007) Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 976.
Specifications
- Peptide NKSLSSFKENEENIQC, corresponding to amino acid residues 84-99 of rat CB1 receptor (Accession P20272). Extracellular, N-terminus.

Scientific Background
Cannabinoids have been used in Eastern medicine for many years as pain relievers.1 Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the major psychoactive compound in marijuana and hashish, has been shown to interact with two specific cannabinoid receptors: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1 receptor) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2 receptor).2 The cannabinoid receptors can be distinguished by their amino acid sequences, signaling mechanisms, and tissue distributions.2 Both receptors belong to the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. CB1 was shown to modulate several Ca2+ and K+ ion channels.2,3
CB1 is primarily expressed in the central nervous system. However, expression of CB1 is also detected in the peripheral terminals, in non-neuronal peripheral tissues such as uterus, testes, spleen, as well as in cells of the immune system.3,4
CB1 is implicated in many cellular functions such as neurotransmitter release, pain relief, cancer, and obesity.5,6 Growth inhibition of tumor cells was demonstrated following mixed CB1/CB2 agonist treatment in both prostate and non-melanoma skin cancers.5,6 Through their interaction with CB1, cannabinoid compounds stimulate appetite for sweets and palatable foods in particular, making CB1 an attractive therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity and eating disorders.7
- Brooks, J.W. and Fraquhar-Smith, M.A. (2003) Br. J. Anaesth. 3, 175.
- Howlett, A.C. (2002) Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 619.
- Howlett, A.C. et al. (2002) Pharmacol. Rev. 54, 161.
- Rueda, D. et al. (2000) Mol. Pharmacol. 58, 814.
- Sarfaraz, S. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65, 1635.
- Casanova, M.L. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Invest. 111, 43.
- Cota, D. et al. (2003) Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 27, 289.

