Overview
- Peptide (C)DRQVPGIARMRLDVR, corresponding to amino acid residues 228-242 of rat CB2 receptor (Accession Q9QZN9). 3rd intracellular loop.

 Western blot analysis of rat RBL basophilic leukemia (lanes 1 and 3), rat C6 brain glioma (lanes 2 and 4) and rat lung (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat RBL basophilic leukemia (lanes 1 and 3), rat C6 brain glioma (lanes 2 and 4) and rat lung (lanes 5 and 6) lysates:1,2,5. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:200).
3,4,6. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody, preincubated with Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR002). Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 4), mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and human Raji B lymphoblastoid cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 6):1-3. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 4), mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and human Raji B lymphoblastoid cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 6):1-3. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody, preincubated with Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR002).
 Expression of CB2 receptor in rat dermisImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded section of rat dermis using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:100). CB2 is expressed in sebaceous glands and ducts of sweat glands in the reticular dermis. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of CB2 receptor in rat dermisImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded section of rat dermis using Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:100). CB2 is expressed in sebaceous glands and ducts of sweat glands in the reticular dermis. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.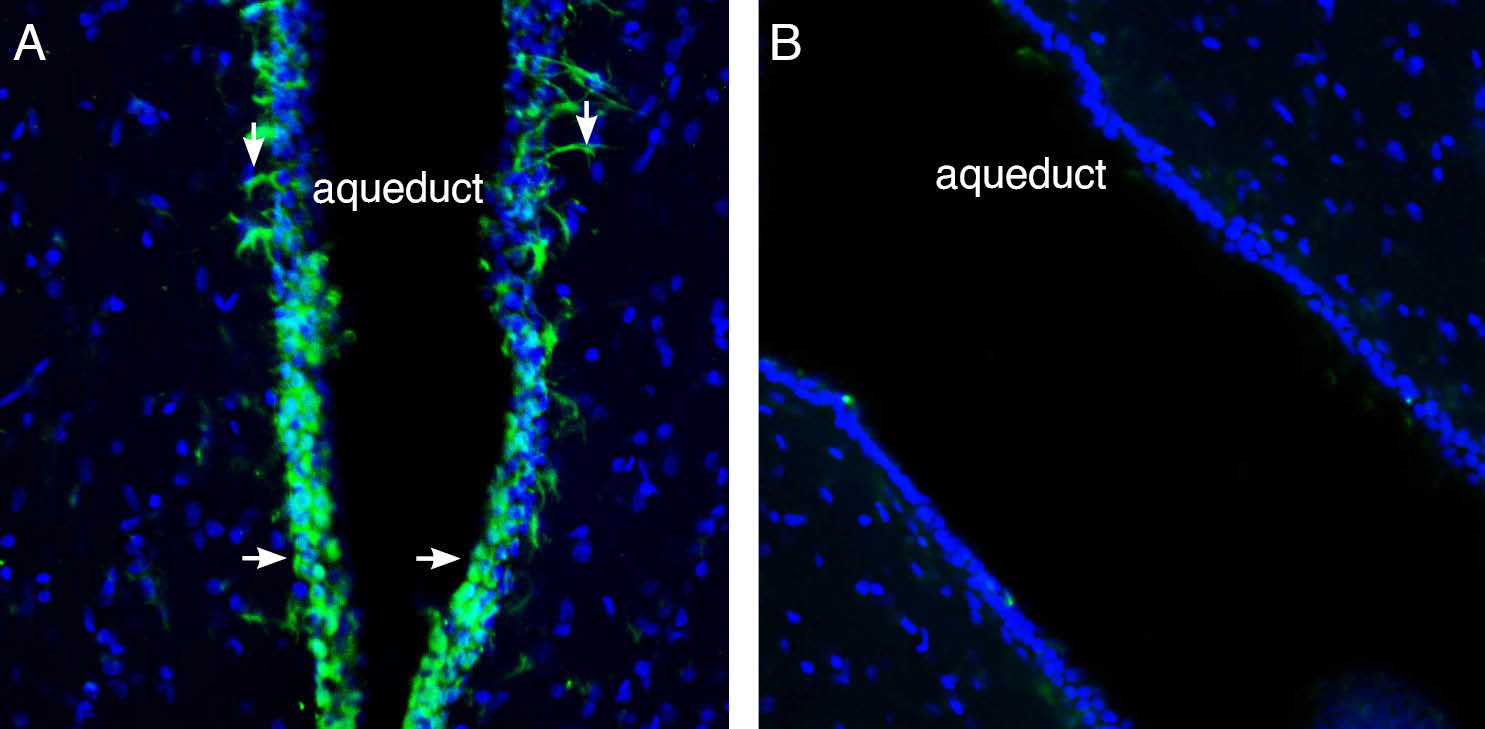 Expression of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in rat midbrain aqueduct.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:400), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. CB2R immunoreactivity (green) appears in a layer lining the wall of the aqueduct (horizontal arrows) and astrocyte-like processes (vertical arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR002), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 in rat midbrain aqueduct.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002), (1:400), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. CB2R immunoreactivity (green) appears in a layer lining the wall of the aqueduct (horizontal arrows) and astrocyte-like processes (vertical arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR002), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Brooks, J.W. and Fraquhar-Smith, M.A. (2003) Br. J. Anaesth. 3, 175.
- Howlett, A.C. (2002) Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68, 619.
- Guo, J. and Ikeda, S.R. (2004) Mol. Pharmacol. 65, 665.
- Wotherspoon, G. et al. (2005) Neuroscience 135, 235.
- Fernandez-Ruiz, J. et al. (2007) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 28, 39.
- Sarfaraz, S. et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65, 1635.
- Sánchez, C. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61, 5784.
Cannabinoids have been used as pain relievers in Eastern medicine for many years.1 To date, two specific cannabinoid receptors have been identified: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2).2 The cannabinoid receptors can be distinguished by their amino acid sequence, signaling mechanisms and tissue distribution.2 Both receptors belong to the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily and are coupled to Gi/0 G protein.2,3
The CB2 receptor is highly expressed in cells of the immune system such as macrophages, lymphocytes natural killer cells and mast cells but has also been shown to be expressed, by both, in situ-hybridization and in immunohistochemistry, in spleen, thymus, and pancreas.1,2,4 CB2 expression in the brain is still much less characterized than that of CB1. Recently, it was demonstrated that CB2 is expressed in the brain and might have a role in controlling fundamental processes such as proliferation and survival of neural cells.5,6
Overexpression of CB2 was reported in several cancers such as prostate, glioma and acute myeloid leukemias.6 In human astrocytoma a direct relationship between CB2 expression and tumor malignancy was demonstrated. Activation of CB2 in vivo by its agonist JWH-133, completely blocked cell growth. In C6 glioma, it was shown that activation of the CB2 by JWH-133 resulted in the internalization of only the CB2 and not CB1 leading to apoptosis of the cells. This may well be a new approach for the treatment of glioma.7
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone is pleased to offer a new antibody directed against an intracellular epitope of the rat CB2 receptor. Anti-Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Antibody (#ACR-002) can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize CB2 receptor in rat, mouse and human.
Applications
Citations
- Pan, J.P. et al. (2011) Brain Res. 1412, 18.
- Gratzke, C. et al. (2010) Eur. Urol. 57, 1093.
