Overview
- Peptide (C)TTKINMDDLQPSENEDKS, corresponding to amino acid residues 848-865 of rat CaV1.2 (Accession P22002). Intracellular loop between domains II and III.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), (1:200).
2. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody, preincubated with Cav1.2/CACNA1C Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC003). Western blot analysis of CaV1.2-transfected Xenopus oocytes (lane 1) and non-transfected oocytes lysates (lane 2):1. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), (1:200) in CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Channel Overexpressed in Xenopus oocytes.
Western blot analysis of CaV1.2-transfected Xenopus oocytes (lane 1) and non-transfected oocytes lysates (lane 2):1. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), (1:200) in CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Channel Overexpressed in Xenopus oocytes.
2. Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody in non-transfected oocytes.- Human cardiac tissue (Crossman, D.J. et al. (2011) PLoS ONE 6, e17901.).
- CaV1.2 transfected HEK-293 cells and mouse heart lysate (Rougier, J.S. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 8829.).
 Expression of CaV1.2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). A. CaV1.2 (red) appears in Purkinje cells (horizontal arrows) and is distributed diffusely in the molecular layer (Mol) including in Purkinje dendrites (vertical arrows). B. Staining of Purkinje nerve cells with mouse anti-Calbindin 28K (green) demonstrates the location of dendrites in the molecular layer. C. Merged image of panels A and B.
Expression of CaV1.2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). A. CaV1.2 (red) appears in Purkinje cells (horizontal arrows) and is distributed diffusely in the molecular layer (Mol) including in Purkinje dendrites (vertical arrows). B. Staining of Purkinje nerve cells with mouse anti-Calbindin 28K (green) demonstrates the location of dendrites in the molecular layer. C. Merged image of panels A and B.- Mouse atrioles (1:300) (Howitt, L. et al. (2013) J. Physiol. 591, 2157.).
- Rat insulinoma cells (RIN) (Parkash, J. (2011) Life Sci. 88, 257.).
- Mouse chromaffin cells (1:200). (Perez-Alvarez, A. et al. (2011) J. Neurochem. 116, 105.).
- Rat mast cells (RBL-2H3 cells, 1μg/5x105 cells). (Yoshimaru, T. et al. (2009) Mol. Immunol. 46, 1267.).
- The control antigen is not suitable for this application.
- Catterall, W.A. et al. (2003) Pharmacol. Rev. 55, 579.
- IUPHAR
- Hu, X.Q. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5337.
- Kreuzberg, U. et al. (2000) Am J. Physiol. 278, H723.
- Allard, B. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275. 25556.
All L-type calcium channels are encoded by one of the CaV1 channel genes. These channels play a major role as a Ca2+ entry pathway in skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles as well as in neurons, endocrine cells and possibly in non-excitable cells such as hematopoetic and epithelial cells. All CaV1 channels are influenced by dihydropyridines (DHP) and are also referred to as DHP receptors.
While the CaV1.1 and CaV1.4 isoforms are expressed in restricted tissues (skeletal muscle and retina, respectively), the expression of CaV1.2 is ubiquitous and CaV1.3 channels are found in the heart, brain and pancreas. Several peptidyl toxins are described that are specific L-type channel blockers, but so far no selective blocker for one of the CaV1 isoforms have been described. These include the Mamba toxins Calcicludine (#SPC-650), Calciseptine (#C-500) and FS-2 (#F-700).
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize CaV1.2 from mouse, rat, and human samples.
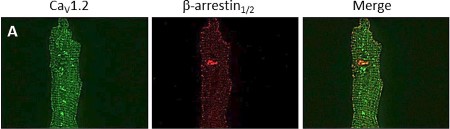
Expression of CaV1.2 in rat cardiomyocytes.Immunocytochemical staining of adult rat cardiomyocytes using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). CaV1.2 staining (green) is observed in a regularly spaced array, as well as surface sarcolemmal staining. β-arrestin staining is in red.Adapted from Hermosilla, T. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7, 10131. with permission of SPRINGER NATURE.
Applications
Citations
 Expression of CaV1.2 in mouse brainImmunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). A. CaV1.2 is detected (green) in the membrane of the soma and the base of the apical dendrites of pyramidal cells in layer II/III of the piriform cortex. B. In neocortex such as the motor cortex, CaV1.2 is also expressed in the shaft of apical dendrites.
Expression of CaV1.2 in mouse brainImmunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). A. CaV1.2 is detected (green) in the membrane of the soma and the base of the apical dendrites of pyramidal cells in layer II/III of the piriform cortex. B. In neocortex such as the motor cortex, CaV1.2 is also expressed in the shaft of apical dendrites.
Adapted from Mukherjee, B. and Yuan, Q. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 35256. with permission of SPRINGER NATURE.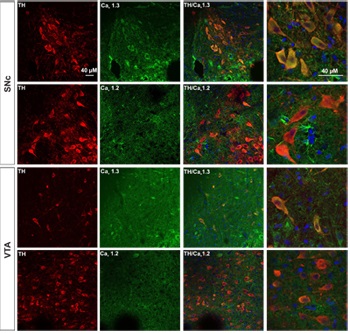 Expression of CaV1.3 in DA neurons from SNc and VTA.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brain sections using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003) or Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), shows that CaV1.3 channel (green) is detected in SNc and VTA regions while little or no CaV1.2 is expressed. CaV1.3 co-localizes with TH (red) in the soma as well as in the proximal dendrites of SNc and VTA DA neurons.
Expression of CaV1.3 in DA neurons from SNc and VTA.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brain sections using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003) or Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), shows that CaV1.3 channel (green) is detected in SNc and VTA regions while little or no CaV1.2 is expressed. CaV1.3 co-localizes with TH (red) in the soma as well as in the proximal dendrites of SNc and VTA DA neurons.
Adapted from Philippart, F. et al. with permission of the Society for Neuroscience.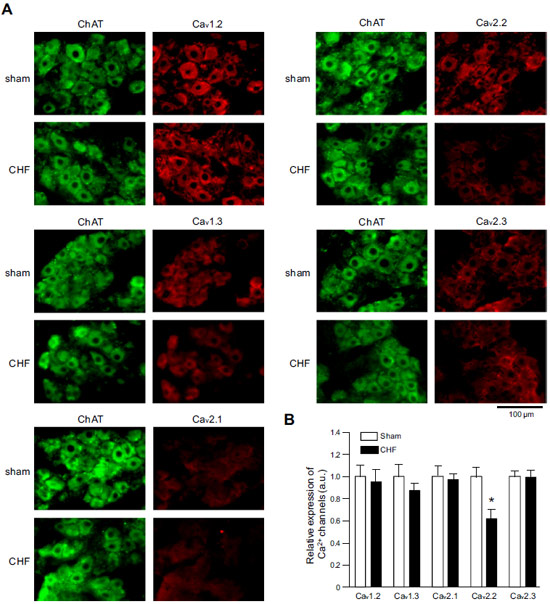 Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.
Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.
Adapted from Tu, H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society. siRNA against CaV1.2 in rat VSMCs significantly decreases its expression.Immunocytochemical staining of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) isolated from nontransfected arteries, sham-transfected arteries, and arteries transfected with siRNA targeting LTCC. Cells were stained using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). Omission of primary antibody was used as a negative control. Bars represent 20 μm.
siRNA against CaV1.2 in rat VSMCs significantly decreases its expression.Immunocytochemical staining of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) isolated from nontransfected arteries, sham-transfected arteries, and arteries transfected with siRNA targeting LTCC. Cells were stained using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003). Omission of primary antibody was used as a negative control. Bars represent 20 μm.
Adapted from Kudryavtseva, O. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.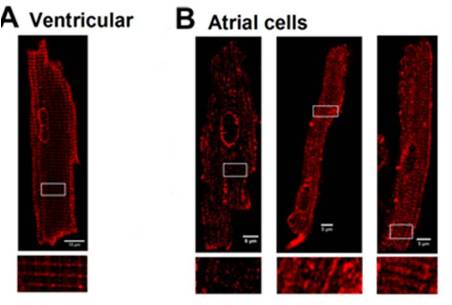 Localization of L-type CaV channels in rat atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes.Immunocytochemical staining of rat ventricular cells (A), and atrial cells (B) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003).
Localization of L-type CaV channels in rat atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes.Immunocytochemical staining of rat ventricular cells (A), and atrial cells (B) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003).
Adapted from Frisk, M. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.
- Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections. Tested in CACNA1C-/- conditional knockout mice.
Jeon, D. et al. (2010) Nat. Neurosci. 13, 482.
- Rat cardiomyocyte lysate.
Jeong, M.H. et al. (2017) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, E1345. - Mouse astrocyte lysate (1:1000).
Cheli, V.T.a et al. (2016) Glia 64, 1396. - Human heart and cardiomyocyte lysates.
Morishima, M. et al. (2016) Circ. J. 80, 1346. - Mouse heart lysate.
Schilling, J.M. et al. (2016) Basic Res. Cardiol. 111, 28. - Mouse heart lysate.
Walton, R.D. et al. (2016) J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 71, 1005. - Mouse cardiac HL-1 cell lysate.
Lu, Y.Y. et al. (2016) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20, 1182. - Mouse eye lysate.
Grabner, C.P. et al. (2015) J. Neurosci. 35, 13133. - Mouse heart lysate (1:500).
Manning, J.R. et al. (2015) Am. J. Physiol. 309, H1336. - Ovine myocyte lysate.
O’Connell, R.P. et al. (2015) PLoS ONE 10, e0133052. - Rat retinae lysate (1:400).
Grimes, W.N. et al. (2015) J. Neurophysiol. 114, 341. - Human artery lysates (1:200).
Harraz, O.F. et al. (2015) J. Gen. Physiol. 145, 405. - Rat heart lysates (1:1000).
Liao, P. et al. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 9262. - Rat brain lysates (1:200).
N’Gouemo, P. et al. (2015) Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 18, pyu123. - Transfected HEK 293 cells (1:5000).
Bourdin, B. et al. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 2854. - Rat primary neonatal ventricular myocardial cell lysates.
Askar, S.F. et al. (2013) Cardiovasc. Res. 97, 171. - HEK-293 cells expressing CaV1.2.
Boczek, N.J. et al. (2013) Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 6, 279. - Rat cortex and cerebral artery lysates.
El-Rahman, R.R. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 304, H58. - Mouse ventricular lysate (1:2000).
Fares, E. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e74719. - Mouse mesenteric and pulmonary arteries (1:200).
Ko, E.A. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 304, C1042. - Rat myocytes.
Li, J. et al. (2013) Int. J. Cardiol. 168, 2109. - Rat primary submucosa cells.
Rehn, M. et al. (2013) Cell Tissue Res. 353, 355. - Mouse synaptosome (1:400).
Saggu, S. et al. (2013) Schizophr. Res. 146, 254. - Rat colon lysates (1:300).
Traini, C. et al. (2013) Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e728. - Rat pituitary lysates.
Tzour, A. et al. (2013) J. Neuroendocrinol. 25, 76. - Rabbit pulmonary vein lysate.
Chang, C.J. et al. (2012) Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 5, 1176. - HEK-293T transfected cells.
Jhun, B.S. et al. (2012) Circ. Res. 110, 59. - Human cardiac tissue.
Crossman, D.J. et al. (2011) PLoS ONE 6, e17901. - Hamster HIT-T15 cell lysate.
Xia, F. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 24685. - Human atrium lysate.
Kreuzberg, U. et al. (2000) Am J. Physiol. 278, H723. - Human atrium lysate.
Brundel, B.J. et al. (1999) Cardiovasc. Res. 42, 443. - Rabbit colonic smooth muscle lysate.
Hu, X.Q. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5337. - Rat heart and skeletal smooth muscle lysates.
Pereon, Y. et al. (1998) Pflugers Arch. 436, 309.
- Mouse cardiomyocyte lysate.
Liang, D. et al. (2019) Int. J. Cardiol. 275, 120. - Rat retinae lysate (1-2 µg / 500 µg protein).
Grimes, W.N. et al. (2015) J. Neurophysiol. 114, 341. - CaV1.2 transfected HEK-293 cells and mouse heart lysate.
Rougier, J.S. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 8829. - Rat pituitary GH4C1 cell lysate.
Hernandez, M.E. et al. (1999) Neuroendocrinology 70, 31.
- Rat brain sections (1:50).
Philippart, F. et al. (2016) J. Neurosci. 36, 7234. - Mouse heart sections.
Willis, B.C. et al. (2016) Circulation 133, 2348. - Mouse eye sections.
Grabner, C.P. et al. (2015) J. Neurosci. 35, 13133. - Mouse brain sections (1:200).
Blosa, M. et al. (2015) J. Physiol. 593, 4341. - Rat intracardiac and stellate ganglia.
Tu, H. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 306, C132. - Mouse cochlear sections.
Lv, P. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 7383. - Rat retinal sections.
Sargoy, A. et al. (2014) PLoS ONE 9, e84507. - Human and mouse fetal lung sections (1:50 - 1:100).
Brennan, S.C. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e80294. - Moue arterial whole mounts (1:300).
Howitt, L. et al. (2013) J. Physiol. 591, 2157. - Rat colon sections (1:200).
Traini, C. et al. (2013) Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e728. - Rat retinal sections (1:250-1:500).
Liu, X. et al. (2013) J. Physiol. 591, 3309. - Mouse brain sections. Also tested in CACNA1C-/- conditional knockout mice.
Jeon, D. et al. (2010) Nat. Neurosci. 13, 482. - Rat kidney sections.
Hansen, P.B. et al. (2001) Circ Res. 89, 630. - Human dental pulp sections.
Allard, B. et al (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 25556. - Mouse spinal cord sections.
Jiang, Z. et al. (1999) Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 3481. - Chinchilla inner ear and cortex sections.
Lopez, I. et al. (1999) Neuroscience 92, 773. - Rat heart and skeletal smooth muscle sections.
Pereon, Y. et al. (1998) Pflugers Arch. 436, 309.
- Mouse cardiomyocytes (1:100).
Liang, D. et al. (2019) Int. J. Cardiol. 275, 120. - Rat cardiomyocytes.
Hermosilla, T. et al. (2017) Sci. Rep. 7, 10131. - Mouse astrocytes (1:200).
Cheli, V.T.a et al. (2016) Glia 64, 1396. - Mouse oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (1:200).
Cheli, V.T. et al. (2016) J. Neurosci. 36, 10853. - Rat adipose-derived stromal cells and rat bone marrow stromal cells.
Forostyak, O. et al. (2016) Stem Cell Res. 16, 622. - Mouse ventricular myocytes.
Fu, Y. et al. (2016) Circulation 133, 388. - Mouse cardiomyocytes (1:300).
Bourdin, B. et al. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 2854. - Rat pinealocytes.
Mizutani, H. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 306, C1008. - Mouse spinal ganglion neurons (SGNs) (1:100-1:500).
Lv, P. et al. (2014) J. Neurosci. 34, 7383. - Rat ventricular and atrial cardiomyocytes.
Frisk, M. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 307, H609. - Rat vascular smooth muscle cells.
Kudryavtseva, O. et al. (2014) Am. J. Physiol. 306, H1287. - Rat primary submucosa cells (1:50).
Rehn, M. et al. (2013) Cell Tissue Res. 353, 355. - Rat insulinoma cells (RIN).
Parkash, J. (2011) Life Sci. 88, 257. - Mouse chromaffin cells (1:200).
Perez-Alvarez, A. et al. (2011) J. Neurochem. 116, 105. - Rat hippocampal neurons.
Lai, M. et al. (2005) Nat. Neurosci. 8, 435. - Guinea pig myocytes.
Ohi, Y. et al. (2001) J. Physiol. 534.2, 313. - Rat osteoblastic sarcoma cells.
Liu, R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8711. - Mouse spermatocytes.
Serrano, C.J. et al. (1999) FEBS Lett. 462, 171. - Rat dorsal root ganglia (DRGs).
Acosta, C.G. and Lopez H.S. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 8337.
- Rat mast cells (RBL-2H3 cells, 1μg/5x105 cells).
Yoshimaru, T. et al. (2009) Mol. Immunol. 46, 1267.
