Overview
- Peptide (C)DNKVTIDDYQEEAEDKD, corresponding to amino acid residues 859-875 of rat CaV1.3 (Accession P27732). Intracellular loop between domains II and III.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), (1:200).
2. Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody, preincubated with Cav1.3/CACNA1D Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC005).- Rat brain membranes (1:200). Human SAN tissue (Le Scouarnec, S. et al. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 15617.).
- Rat cerebral cortex, thalamus, cerebellum, hippocampus, and spinal cord lysates (Kim, S. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 32877.).
- Rat brain sections.
- Mouse SAN cells (Le Scouarnec, S. et al. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 15617.).
All L-type calcium channels are encoded by one of the CaV1 channel genes. These channels play a major role as a Ca2+ entry pathway in skeletal cardiac and smooth muscles as well as in neurons, endocrine cells and possibly in non-excitable cells such as hematopoetic and epithelial cells. All CaV1 channels are influenced by dihydropyridines (DHP) and are also referred to as DHP receptors. While the CaV1.1 and CaV1.4 isoforms are expressed in restricted tissues (skeletal muscle and retina, respectively), the expression of CaV1.2 is ubiquitous.1,2
The CaV1.3 channels are also expressed, as are other L-type channels, in neurons and neuroendocrine cells. However, accumulated data has shown the expression of CaV1.3 in heart and suggests that it plays a major role in the generation of cardiac pacemaker activity.3,4
Several peptidyl toxins have been described that are specific L-type channel blockers. These include the Mamba toxins Calcicludine (#SPC-650), Calciseptine (#C-500) and FS-2 (#F-700). So far no selective blocker for one of the CaV1 isoforms has been described.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
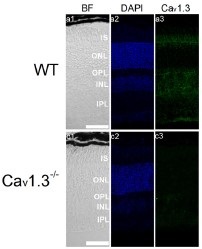
Knockout validation of Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody in mouse eye sections.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse eye sections using Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005). CaV1.3 immunoreactivity (green) is detected in major retinal layers (upper panel). CaV1.3 is not detected in CaV1.3-/- mice.Adapted from Shi, L. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11, 232. with permission of Frontiers.
