Overview
- Peptide (C)SASQERSLDEGVSIDG, corresponding to amino acid residues 892-907 of rat CaV2.3 (Accession Q07652). Intracellular loop between domains II and III.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006), (1:200).
2. Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody, preincubated with Cav2.3/CACNA1E Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC006).
 Expression of CaV2.3 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). CaV2.3 (red) appears in both soma and dendritic trees of several Purkinje cells. Staining of neurofilament 200 (green) in the same brain section demonstrates the relationship between axons passing through the granule layer and the Purkinje cells.
Expression of CaV2.3 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum with Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). CaV2.3 (red) appears in both soma and dendritic trees of several Purkinje cells. Staining of neurofilament 200 (green) in the same brain section demonstrates the relationship between axons passing through the granule layer and the Purkinje cells.
- Mouse spiral ganglion (1:50) (Chen, W.C. et al. (2011) Hear. Res. 278, 52.).
Human sperm cells (1:100) (Trevino, C.L. et al. (2004) FEBS Lett. 563, 87.).
- Tsunemi, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 7214.
- Gasparini, S. et al. (2001) J. Neurosci.21, 8715.
- Lanzafame, A.A. et al. (2003) Receptors Channels 9, 241.
Voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (CaV channels) are pivotal players in many physiological roles such as secretion, contraction, migration and excitation.1
The voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels are composed of several subunits; α1, β, α2δ and γ. CaV channels were originally divided into six physiological types: L-, N-, P-, Q-, R-, and T-type.1
The CaV2.3 (formerly named α1E) protein, forms the R-type channels. R-type channels are highly sensitive to both SNX-482 (#RTS-500) and NiCl2. CaV2.3 channels were shown to mediate fast excitatory transmission in several synapses including the hippocampus.2
CaV2.3 channels can be modulated by the muscarinic G-protein coupled receptors.
In HEK-293 cells, expressing CaV2.3 channels, the R-type channel was shown to be both facilitated and inhibited by m1 and m2 muscarinic receptors. However, inhibition was much weaker than facilitation for the m1 receptor, while for m2 receptors, inhibition was much more pronounced than activation.3
Facilitation and inhibition by the same receptors was probably exerted via different pathways as was indicated by their response to various inhibitors.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer an antibody raised against an epitope of the rat CaV2.3 channel. Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006) can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize CaV2.3 from human, mouse and rat samples.
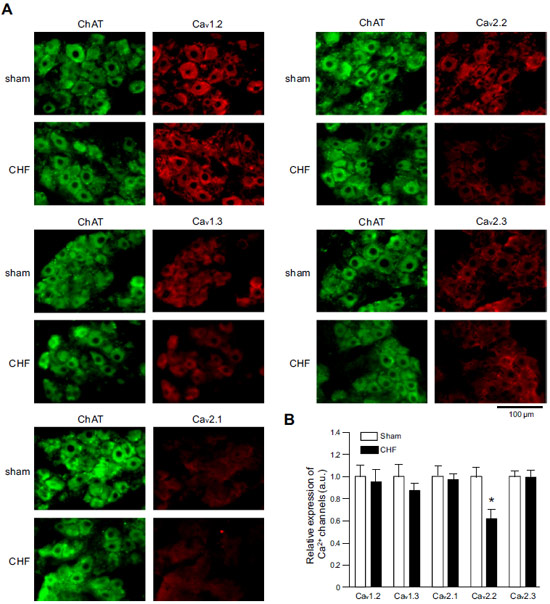 Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.Adapted from Tu, H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.
Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.Adapted from Tu, H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.Applications
Citations
- Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate. Tested in CaV2.3-/- mice.
Saegusa, H. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 6132.
- Mouse brain lysate. Tested in CaV2.3-/- mice.
Saegusa, H. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 6132.
- Mouse spiral ganglion (1:50).
Chen, W.C. et al. (2011) Hear. Res. 278, 52. - Human sperm cells (1:100).
Trevino, C.L. et al. (2004) FEBS Lett. 563, 87.
- Rodriguez-Tapia, E.S. et al. (2017) Exp. Physiol. 102, 299.
- Shakeri, B. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 32835.
- Ohta, T. et al. (2010) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 394, 464.
- Murakami, M. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 354, 1016.
- Shiraiwa, T. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 355, 1019.
- Fisher, T.E. et al. (2000) FEBS Lett. 482, 131.
