Overview
- Peptide CSWWHSDMTAKAQK, corresponding to amino acid residues 942-955 of rat CaVα2δ3 (Accession Q8CFG5). Extracellular.

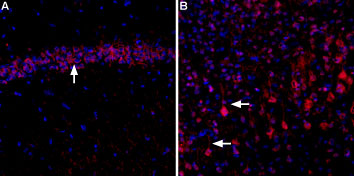 Expression of CaVα2δ3 in rat hippocampus and cortexImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA3 region (A) and rat neocortex (B) using Anti-CACNA2D3 (CaVα2δ3) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#ACC-103-AR). In both, A and B, CaVα2δ3 staining (red) appears in pyramidal neurons (arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of CaVα2δ3 in rat hippocampus and cortexImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal CA3 region (A) and rat neocortex (B) using Anti-CACNA2D3 (CaVα2δ3) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#ACC-103-AR). In both, A and B, CaVα2δ3 staining (red) appears in pyramidal neurons (arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Catterall, W.A. (2000) Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 16, 521.
- Qin, N. et al. (2002) Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 485.
- De Jongh, K.S. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 14738.
- Sipos, I. et al. (2000) Pflug. Arch. 439, 691.
- Dolphin, A.C. (2009) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 19, 237.
- Cooper C.L. et al. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262, 509.
- Kurshan P.T. (2009) Nat. Neurosci. 12, 1415.
- Palmieri, C. et al. (2012) Br. J. Cancer 108, 375.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ (CaV) channels are ubiquitously expressed and function as Ca2+ conducting pores in the plasma membrane1. On the basis of their voltage activation properties, CaV channels can be further divided into two broad groups: the low (T-type) and high (L, N, P, Q and R-type) threshold-activated channels2. HVA channels are heteromultimers composed of four independently encoded proteins, the pore-forming α1 subunit, which triggers Ca2+ flow across the membrane, and the auxiliary subunits α2δ, γ, and β3. The Ca2+ channel α2δ subunit is a heavily glycosylated protein that is encoded by a single gene and post-translationally cleaved to yield α2 and δ subunits linked by a disulfide bond with a single transmembrane segment4. The α2δ subunit regulates many functional aspects of Ca2+ channels, such as gating, regulating voltage dependent kinetics, and increasing functional channel density on the plasma membrane5.
There are four proteins that comprise CaVα2δ: CaVα2δ1, CaVα2δ2, CaVα2δ3 and CaVα2δ46. The CaVα2δ3 subunit is predominantly expressed in neuronal tissue. The CaVα2δ3 subunit regulates all classes of HVA calcium channels. The Caα2δ3 subunits in the nerve terminal function in synaptic morphogenesis and cytoskeletal organization, and that this role is independent of their function in α1 subunit localization and physiology.
CaVα2δ3 is likely to be the primary presynaptic α2δ isoform mediating morphological development of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), since null alleles have such a large effect on NMJ development and abolish all action-potential evoked transmission7. Recent study shows that methylation-dependent transcriptional silencing of CaVα2δ3 may contribute to the metastatic phenotype of breast cancer8.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CACNA2D3 (CaVα2δ3) (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-103) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize CaVα2δ3 from rat, mouse and human samples.
Anti-CACNA2D3 (CaVα2δ3) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#ACC-103-AR) is directly labeled with an ATTO-594 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-594 fluorescent label belongs to the class of Rhodamine dyes and can be used with fluorescent equipment typically optimized to detect Texas Red and Alexa-594. Anti-CACNA2D3 (CaVα2δ3) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody has been tested in immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry applications and is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.

