Overview
- Peptide CHVEGPQERARVAHS, corresponding to amino acid residues 581-595 of rat CaV3.2 (Accession number Q9EQ60). Intracellular loop between domains D1 and D2.
 Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-CaV3.2 (CACNA1H) Antibody (#ACC-025), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-CaV3.2 (CACNA1H) Antibody (#ACC-025), (1:200).
2. Anti-CaV3.2 (CACNA1H) Antibody, preincubated with Cav3.2/CACNA1H Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC025).- Rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) lysate (1:200). Human CaV3.2 transfected in HEK-293 cells (1:100) (Markandeya, Y.S. et al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286, 2433.).
- Rat brain lysates (5 μg) (Weiss, N. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 2810.).
- Mouse cerebellum (1:100), rat DRG (1:50).
- Rat DRG primary culture (1:100-1:200).
T-type Ca2+ channels play an important role in many cellular processes such as hormone secretion, neurotransmitter release and cell differentiation. T-type channels are also known to participate in the pacemaker activities of the heart and neurons including thalamic neurons.1
Three genes encoding T-type Ca2+ channels have been cloned and designated as CaV3.2 (CACNA1H), CaV3.1 (CACNA1G) and CaV3.3 (CACNA1I).1-3
The CaV3.2 channel is widely expressed in various tissues such as the brain, heart, liver and testis.
Involvement of CaV3.2 Ca2+ channels in several pathologies has been described. Overexpression of the CaV3.2 channel was described in prostate cancer cells that are associated with more aggressiveness, invasiveness and poor prognosis.4 Several point mutations discovered in the CaV3.2 channel that affect gating of the channel were found to be associated with Childhood Absence Epilepsy.5 One year old mice, deficient in CaV3.2 channel, exhibited severe cardiac pathology, fibrosis, necrosis, lymphocyte infiltration and abnormal coronary function compared to wild-type mice.6
Recently, it has been demonstrated that T-type channels are expressed in DRG neurons and that small and medium-diameter primary afferent neurons in the dorsal horn expresses almost exclusively the CaV3.2 Ca2+channels. This might indicate a possible role for CaV3.2 in nociception.7
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
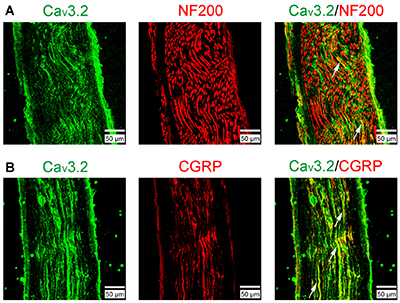
Expression of CaV3.2 in Rat Sural Nerve.Immunohistochemical staining of rat sural nerve sections using Anti-CaV3.2 (CACNA1H) Antibody (#ACC-025). A. CaV3.2 staining (green) partially colocalizes with neurofilament 200. B. CaV3.2 staining (green) significantly colocalizes with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, red), a marker for nociceptive peptidergic fibers.Adapted from Chen, W. et al. (2018) Front. Mol. Neurosci. 11, 24. with permission of Frontiers.
