Overview
- Peptide CIKRLWQADVPAGR, corresponding to amino acid residues 87-100 of rat CACNG6 (Accession Q8VHW3).

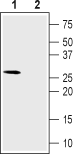 Western blot analysis of rat skeletal muscle lysate:1. Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-112), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat skeletal muscle lysate:1. Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-112), (1:200).
2. Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with CACNG6 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC112).
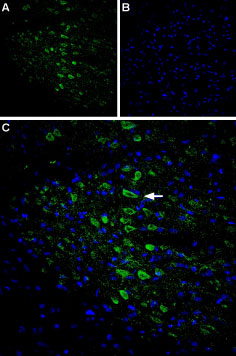 Expression of CaVγ6 (CACNG6) in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat cingulate cortex using Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-112), (1:400). A. CaVγ6 staining (green) appears in the pyramidal layer (arrow). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merged images of A and B.
Expression of CaVγ6 (CACNG6) in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat cingulate cortex using Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-112), (1:400). A. CaVγ6 staining (green) appears in the pyramidal layer (arrow). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merged images of A and B.
- Lee, J.S. et al. (2010) BMC Med. Genet. 11, 138.
- Thomas, G. et al. (2009) FASEB J. 23, 998.
- Chen, R.S. et al. (2007) Cell. Biochem. Biophys. 47, 178.
The calcium channel voltage-dependent gamma subunit 6 encoded by the CACNG6 gene, encodes an integral membrane protein. Its role is to stabilize the calcium channel during the channels inactive state. This subunit is responsible for decreasing Ca2+ currents when it is co-expressed with the low voltage activated Ca2+ channel subunit1,2.
The calcium channel γ subunits comprise eight members that share a common topology.
This family is divided in three clusters: The first- γ1 and γ6, second γ5 and γ7 and third γ2,3,4,8.
CaVγ6 protein is predominantly expressed in striated muscle cells. It is also expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscles and slightly in the brain as a separate isoform.
CaVγ6 structure includes four transmembrane domains (TM) with short intracellular N- and C-terminus. The first TM with a specifically motif- GxxxA is critical for CaVγ6 inhibitory function2. Phylogenetic analysis has suggested that all γ subunits developed from a single ancestral gene through tandem repeat and chromosome duplication3.
Voltage-dependent calcium channels are important regulators of calcium influx and are important for several physiological processes including- synaptic transmission, muscle contraction, neurogenesis, hormone secretion, cell motility, cell division and development.
Several recent studies have shown a negative correlation of CaVγ6 gene expression to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, responses of the human airway epithelium following injury and parenchyma in lung tissues1,3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat CaVγ6. Anti-CACNG6 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-112) can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope and is thus ideal for detecting CaVγ6 in living cells. It has been designed to recognize CaVγ6 from rat, mouse and human samples.
