Overview
- Peptide CETPRIRGTGTRELE, corresponding to amino acid residues 39-53 of mouse Gastrin/cholecystokinin type B receptor (Accession P56481). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with CCKBR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR042).
 Expression of Cholecystokinin B receptor in rat stomachImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded rat stomach sections using Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:100). Cholecystokinin B receptor (brown) is expressed in both parietal cells (black arrows) and in chief cells (red arrows) of the gastric mucosa. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Cholecystokinin B receptor in rat stomachImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded rat stomach sections using Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:100). Cholecystokinin B receptor (brown) is expressed in both parietal cells (black arrows) and in chief cells (red arrows) of the gastric mucosa. Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain. Expression of CCKBR in rat hypothalamus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat dorsomedial hypothalamus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in neurons (vertical arrows) and along the wall of 3rd ventricle (horizontal arrow). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with CCKBR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR042), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). 3rd V = Third ventricle.
Expression of CCKBR in rat hypothalamus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat dorsomedial hypothalamus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in neurons (vertical arrows) and along the wall of 3rd ventricle (horizontal arrow). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with CCKBR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR042), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). 3rd V = Third ventricle.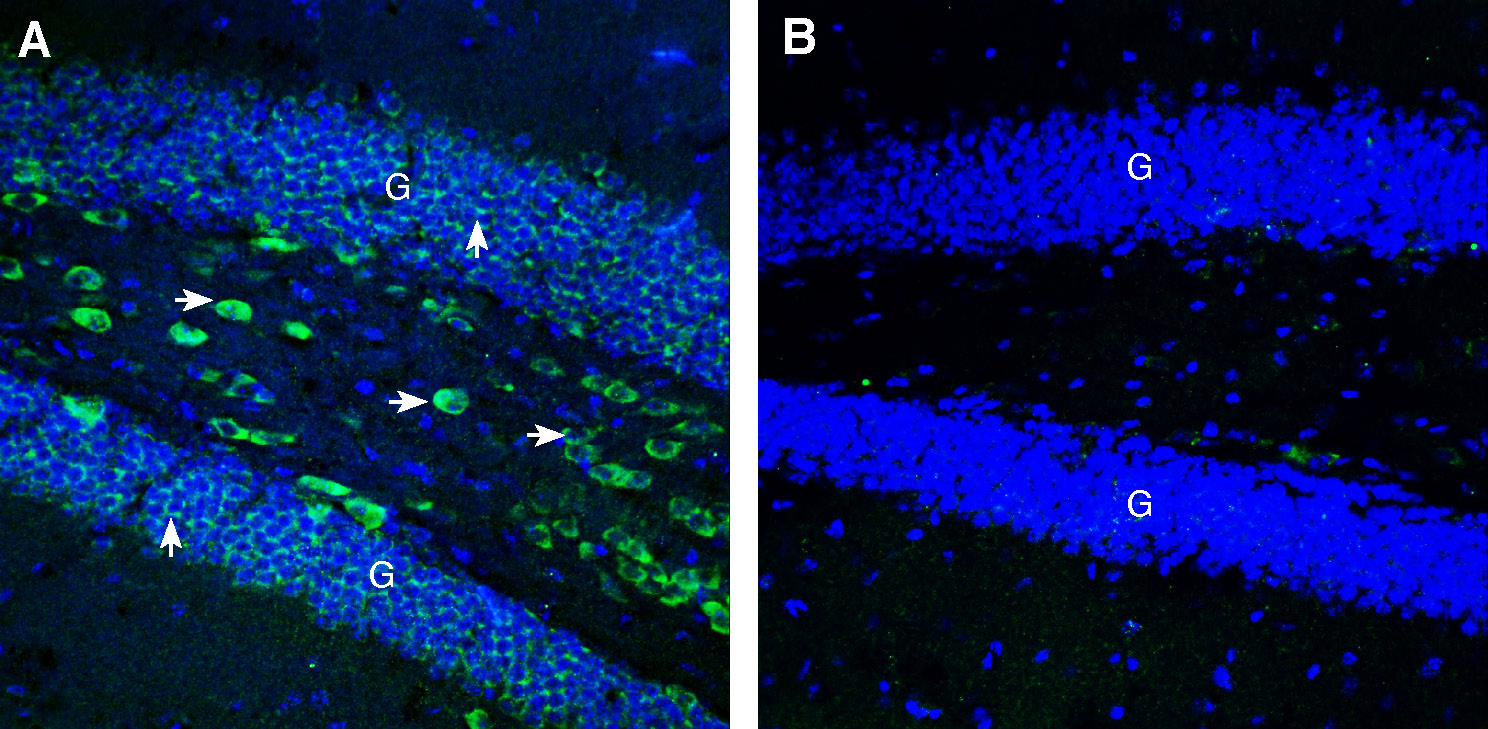 Expression of CCKBR in mouse hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in the granule layer (G, vertical arrows) and in interneurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with CCKBR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR042), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of CCKBR in mouse hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in the granule layer (G, vertical arrows) and in interneurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with CCKBR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR042), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
 Cell surface detection of Cholecystokinin B receptor by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Cholecystokinin B receptor by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + goat-anti-rabbit-PE.
___ Cells + Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042), (5μg) + goat-anti-rabbit-PE.- The control antigen is not suitable for this application.
- Noble, F. et al. (1999) Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 745.
- Dufresne, M. et al. (2006) Physiol Rev. 86, 805.
Cholecystokinin B receptor (CCKBR), also known as the Gastrin receptor and CCKR2, belongs to the 7-transmembrane domain, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, and is one of the two receptors that mediates the effects of the cholecystokinin (CCK) and gastrin peptides1,2.
CCK and gastrin are related linear peptides that occur in different forms but share the last five C-terminal amino acid residues. CCK regulates several nutritional-related activities such as stimulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion or the regulation of intestinal transit, while gastrin's main function is the stimulation of gastric acid secretion1,2.
Both CCKBR and the other CCK receptor (CCKAR or CCK1R) are coupled to a Gq/11 protein that activates phospholipase C (PLC) and leads to production of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3), and intracellular Ca2+mobilization.
CCKBR was originally identified in the brain (and hence its name, type B for Brain) where it is widely distributed, notably in the cerebral cortex and striatum. In the periphery, CCKBR is most notably expressed in acid secreting cells in the mucosa of the stomach. The tissue distribution of CCKBR corresponds to the proposed roles of the receptor which include anxiety, pain perception, gastric acid secretion, and growth and differentiation of the gastric mucosa1,2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CCKBR (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-042) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse cholecystokinin B receptor. The antibody can be used in western blot, indirect flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize CCKBR from mouse, rat, and human samples.
