Overview
- Peptide CVHRLGRVLRRKLGED, corresponding to amino acid residues 102-117 of rat CLC-1 (Accession P35524). Cytoplasmic, N-terminal part.
 Western blot analysis of rat skeletal muscle membranes:1. Anti-CLC-1 (CLCN1) Antibody (#ACL-005), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat skeletal muscle membranes:1. Anti-CLC-1 (CLCN1) Antibody (#ACL-005), (1:200).
2. Anti-CLC-1 (CLCN1) Antibody, preincubated with CLC-1/CLCN1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CL005).
- Jentsch, T.J. et al. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 503.
- Babini, E. and Pusch, M. (2004) Physiology 19, 293.
- Koch, M.C. et al. (1992) Science 257, 797.
CLC-1 is a member of the voltage-dependent Cl- channel (CLC) family that includes nine known members in mammals. CLC channels can be classified as plasma membrane channels and intracellular organelle channels. The first group includes the CLC-1, CLC-2 CLC-Ka and CLCKb channels. The second group comprises the CLC-3, CLC-4, CLC-5, CLC-6 and CLC-7.
CLC channels that function in the plasma membrane are involved in the stabilization of membrane potential and in transepithelial transport. The presumed function of the intracellular CLC channels is support of the acidification of the intraorganellar compartment. In this regard, recent reports indicate that ClC-4 and ClC-5 (and by inference ClC-3) can function as Cl-/H+ antiporters.1, 2
The functional unit of the CLC channels is a dimer with each subunit forming a proper pore. Although the crystal structure of bacterial CLC channels was resolved, the topology of the CLC channels is complex and has not been fully elucidated. It is generally accepted that both the N- and C- terminus domains are intracellular while the number and configuration of the transmembrane domains vary greatly between different models. 1,2
The ClC-1 channel is almost exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle where it has a dominant role in maintaining the membrane potential at rest and is important for repolarization of the skeletal muscle cells.
Mutations in the ClC-1 gene result in myotonia congenita, a condition in which an increase in the excitability of skeletal muscle leads to repetitive action potentials, stiffness, and delayed relaxation. The disease can be either autosomal dominant (Thomsen's disease), or recessive (Becker's myotonia).3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CLC-1 (CLCN1) Antibody (#ACL-005) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot analysis. It has been designed to recognize CLC-1 from rat, mouse, and human samples.
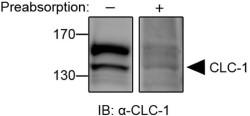
Expression of CLC-1 in rat skeletal muscle.Western blot analysis of rat skeletal muscle using Anti-CLC-1 (CLCN1) Antibody (#ACL-005), (left lane). Detection of CLC-1 is abolished when the antibody is preincubated with the control antigen (right lane).Adapted from Chen, Y.A. et al. (2015) Sci. Rep. 5, 10667. with permission of SPRINGER NATURE.
Applications
Citations
- Rat muscle lysate.
Chen, Y.A. et al. (2015) Sci. Rep. 5, 10667.
