Overview
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
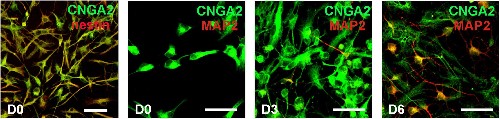
Expression of CNGA2 in mouse neural stem cells.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse neural stem cells with Anti-CNGA2 Antibody (#APC-045). CNGA2 staining (green) co-localizes with Nestin (red), a neural stem cell marker and MAP2 (red), a neuronal marker at different differentiation stages.Adapted from Podda, M.V. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e73246. with permission of PLoS.
Specifications
- Peptide (C)KQNHEDDYLSDGINTPEP, corresponding to amino acid residues 643-660 of rat CNGA2. (Accession Q00195). Intracellular, C-terminus.
Applications
- Rat brain membranes (1:200). Addition of 0.1-0.5% Tween-20 to the antibody solution may strengthen the signal.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CNGA2 Antibody (#APC-045), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-CNGA2 Antibody (#APC-045), (1:200).
2. Anti-CNGA2 Antibody, preincubated with CNGA2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC045).
- Rat cerebellum frozen sections and mouse lateral ventricle heart sections.
- Rat cerebellum primary culture (1:100).
Scientific Background
Cyclic nucleotides are important second messengers in many cellular functions such as visual transduction, and relaxation of smooth muscle cells. Cyclic nucleotides exert their cellular functions through three major classes of cellular receptors, one of them is the cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels.1 The CNG channels are non-selective cation channels facilitating the influx of Na+ and Ca2+ ions, following activation by intracellular cyclic nucleotides.2 In vertebrates, six members of the CNG channel family were identified and grouped according to sequence homology into two subtypes, CNGA and CNGB. To date, four types of the a subunits (CNGA1-4) and two b subunits (CNGB1, CNGB3) have been characterized.3
Native CNG channels are composed of a and b subunits in a tetrameric configuration. Each subunit contains 6 TM domains and intracellular cAMP or cGMP binding domains, but are also modulated by other factors including phosphorylation and calmodulin.4 In a heterologous expression system, only the a subunits are capable of forming functional homomeric channels.
CNG ion channels are essential in visual and olfactory signal transduction.
CNG channels were originally detected in rod and cone photoreceptors and olfactory receptor cells, where they mediate the transduction of external sensory stimuli into neuronal activity.5
CNGA2 is predominantly expressed in olfactory neurons (the olfactory type receptor). However, electrophysiological and molecular data indicate that CNGA1, and especially CNGA2, are widely distributed and functionally active in many regions of the brain, including the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem.6
