Overview
- Peptide (C)EVKELAPHPSGLR, corresponding to amino acid residues 170-182 of rat Connexin-36 (Accession O70610). Intracellular loop.
- Rat and mouse brain membranes (1:200-1:1000).
 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-Connexin-36 Antibody (#ACC-209), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-Connexin-36 Antibody (#ACC-209), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Connexin-36 Antibody, preincubated with Connexin-36 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC209).
- Rat spinal cord sections (1:300).
The structural unit of the gap junctions is the connexon. Connexons are hexameric structures, formed by transcellular channels composed of connexins. Connexins (Cx) share a common structural basis, which is a four-transmembrane spanning protein, a cytoplasmic loop, two extracellular loops (E1–E2), one intracellular amino-(NT domain) and a carboxy-terminal (CT domain) region1.
Connexin 36 (Cx36) is predominantly expressed in mammalian neuronal cells2. Cx36 is expressed in a variety of mammalian brain regions, but expression is particularly notable in the inferior olive, cerebellar cortex, olfactory bulbs, several brainstem nuclei, the CA3 subregion of the hippocampus and reticular thalamic nuclei3. Outside of the central nervous system, Cx36 also appears in motoneurons of adult rat spinal cord 4.
Studies have shown that Cx36 is involved in some neural functions, including neuronal neurogenesis, neural fertility control and regulation of waking and sleep states, and also Cx36 plays an important role in N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated neuronal death following neuronal injury5. A number of studies performed in humans and animals have confirmed the role of Cx36 in the generation and maintenance of seizure activity6.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
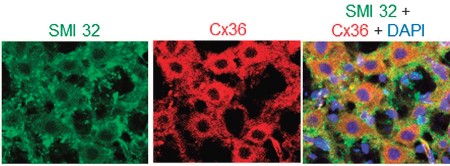
Expression of Cx36 in rat brainstem.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brainstem sections using Anti-Connexin-36 Antibody (#ACC-209). Cx36 staining (red) is localized to hypoglossal motoneurons, as is SMI 32, a motoneuron marker (green). DAPI is used to stain nuclei.Adapted from Corsini, S. et al. (2017) Cell Death Dis. 8, e2881. with permission of Nature Publishing Group.
