Overview
- Peptide CNVNTHEKVKTALN, corresponding to amino acid residues 127 - 140 of human Calcitonin Receptor-Like Receptor (Accession Q16602). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG), lung and heart membrane lysates; mouse heart and brain membrane lysates; human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell lysate (1:200-1:1000).
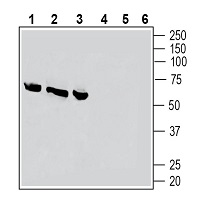 Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysates (lanes 1 and 4), rat lung membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and rat heart membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-CRLR/CALCRL (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-060), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysates (lanes 1 and 4), rat lung membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and rat heart membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-CRLR/CALCRL (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-060), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-CRLR/CALCRL (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with CRLR/CALCRL (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR060).
- Rat and mouse brain sections (1:200).
- Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells (2.5 µg).
Calcitonin Receptor-Like Receptor 1 (CRLR or CGRPR) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the peptide hormone calcitonin and is involved in maintenance of calcium homeostasis, particularly with respect to bone formation and metabolism1.
When engaged with its substrate, calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP), CGRPR activates cAMP-dependent pkA and PI3 kinase, which eventually leads to complex inhibitory as well as facilitator actions on Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor1.
CGRP receptor is a heterodimer composed of two proteins: a 7‐transmembrane domain type 2 G-protein coupled receptor called calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR), and receptor-activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), a single-membrane-pass protein. RAMP1 serves as a transporter for CRLR to the cell surface and its absence leads to failure of binding with CRLR2.
CGRP and CGRPR are ubiquitously expressed and their interaction is related to various diseases and health states such as migraines3 and Alzheimer's disease1.
