Overview
- Peptide (C)EGISIYTSDNYTEE, corresponding to amino acid residues 2-15 of human CXCR4 (Accession P61073). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with CXCR4 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CR014).
 Expression of CXCR4 in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum frozen section using Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:100). CXCR4 is expressed in Purkinje cell bodies and axonal prolongations (arrows). Hoechst 33342 is used as the counterstain.
Expression of CXCR4 in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum frozen section using Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:100). CXCR4 is expressed in Purkinje cell bodies and axonal prolongations (arrows). Hoechst 33342 is used as the counterstain.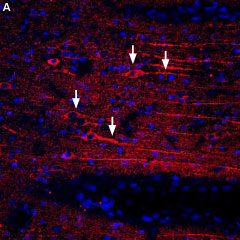 Expression of CXCR4 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat temporal cortex using Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:400) followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and streptavidin labeled with Cy3. A. CXCR4 staining (red) appears in neuronal soma and processes (arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of CXCR4 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat temporal cortex using Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (1:400) followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and streptavidin labeled with Cy3. A. CXCR4 staining (red) appears in neuronal soma and processes (arrows). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Human vascular smooth muscle cells (hVSMCs) (Gao, X. et al. (2018) Sci. Rep. 8, 2730.).
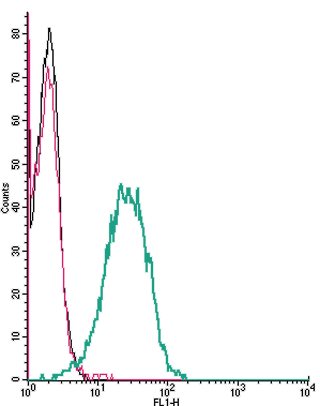 Cell surface detection of CXCR4 by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of CXCR4 by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.
___ Cells +Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014), (2.5μg) + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.- The blocking peptide is not suitable for this application.
- Raman, D. et al. (2007) Cancer Lett. 256, 137
- Burger, J.A. and Kipps, T.J. (2006) Blood 107, 1761.
- Loetscher, P. et al. (2000) Adv. Immunol. 74, 127.
- Feng, Y. et al. (1996) Science 272, 872.
- Wong, D. and Korz, W. (2008) Clin. Cancer. Res. 14, 7975.
- Vila-Coro, A.J. et al. (1999) FASEB J. 13, 1699.
- Holland, J.D. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 4117.
- Richardson, R.M. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 15867.
- Zou, Y.R. et al. (1998) Nature 393, 595.
- Heesen, M. et al. (1996) J. Immunol. 157, 5455.
- Habasque, C. et al. (2002) Mol. Hum. Reprod. 8, 419.
- Murdoch, C, et al (2003) Immunological Reviews. 177:175-184.
Chemokines are small molecular weight, soluble secreted proteins that bind and activate their respective G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), chemokine receptors in order to evoke a cellular response resulting in migration or chemotaxis1.
The chemokine system involves more than 40 chemokines and 18 chemokine receptors. The receptors are designated CXCR1-5, CCR1-11, XCR1 and CX3CR1, based on their specific ligand preference2.
Chemokine receptors are present on many different cell types. They were initially detected on leukocytes, where they were found to play an important role in the migration of these cells to inflammation sites3.
CXCR4 was originally identified as an orphan receptor, and soon gained much attention when it was discovered as a coreceptor for HIV-14. Besides from being involved in HIV-1 infection/progression, CXCR4 is found to be upregulated in many different cancers/tumors and has evolved to become a target for the development of antagonists5. CXCL12 (SDF-1α) is the sole ligand for CXCR4. Following binding of its ligand, CXCR4 undergoes dimerization and activates Gi G-proteins6,7. However downstream activation through CXCR4 could also occur through other G-proteins and non-G-proteins5. The down regulation of the CXCR4 receptor is initiated by phosphorylation of its cytoplasmic tail, which is followed by the binding of arrestin. The receptor is then internalized through endocytosis and degraded in the lysosome. Downregulation of CXCR4 could also occur through the stimulation of other GPCRs8.
The distribution of CXCR4 is quite broad and involves the central nervous system (CNS)9, spleen10, testes11, hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells12.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CXCR4 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACR-014) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the human CXCR4 chemokine receptor. The antibody can be used for western blot, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize CXCR4 from rat, mouse and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Human vascular smooth muscle cells (hVSMCs).
Gao, X. et al. (2018) Sci. Rep. 8, 2730. - Human vascular smooth muscle cells (hVSMCs).
Albee, L.J. et al. (2017) J. Am. Heart Assoc. 6, e006575.
