Overview
- Peptide (C)DDLERQNWSRPFNGSE, corresponding to amino acid residues 11-26 of rat DRD2 (Accession P61169). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat striatum and hippocampus membranes (1:200) and rat and mouse whole brain membranes (1:200).
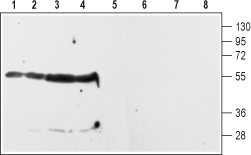 Western blot analysis of rat striatum (lanes 1 and 5) and hippocampus (lanes 2 and 6) membranes and of rat (lanes 3 and 7) and mouse (lanes 4 and 8) whole brain lysates:1-4. Anti-D2 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat striatum (lanes 1 and 5) and hippocampus (lanes 2 and 6) membranes and of rat (lanes 3 and 7) and mouse (lanes 4 and 8) whole brain lysates:1-4. Anti-D2 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-002), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-D2 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with D2 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-DR002).
Rat brain sections (1:100), (see Yang, Y.L. et al. (2019) Front. Neurosci. 13, 195.).
The D2 dopamine receptor (DRD2) is one of five receptors that mediate the effects of the catecholamine neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine regulates a variety of functions including locomotor activity, emotion, positive reinforcement, food intake, and endocrine regulation. The dopaminergic system has been extensively studied in the last thirty years mainly because its dysregulation has been linked to several neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases including Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia.1
All five dopamine receptors belong to the 7-transmembrane domain, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily.
Historically, the five receptors have been divided into two subfamilies based on pharmacological and structural considerations: the D1-like subfamily (that includes the D1 and D5 subtypes) and the D2-like subfamily (that includes the D2-, D3- and D4 subtypes).1
The D1-like receptors are coupled to Gs-type G proteins and enhance adenylate cyclase activity while the D2-like receptors are coupled to Gi-type G proteins and inhibit adenylate cyclase activity.1
D2 receptor expression in the brain is largely confined to the striatum, prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus.1
Dysregulation of D2 receptor function has been implicated in several disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, Parkinson's disease, and restless legs syndrome. Consistent with this, treatments that either block or activate the D2 receptor have been developed to treat these diseases.2
