Overview
- Peptide CGAENSTGVNRARPH, corresponding to amino acid residues 15-29 of rat DRD3 (Accession P19020). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Whole rat brain and rat striatum membranes (1:200) and mouse brain membranes (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of whole rat brain (lanes 1 and 3) and striatum (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-003), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of whole rat brain (lanes 1 and 3) and striatum (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-003), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-DR003). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-003), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-003), (1:200).
2. Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-DR003).
- Rat brain sections (frozen) (1:100).
The D3 Dopamine Receptor (D3 receptor) is one of five receptors that mediate the effects of the catecholamine neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine regulates a variety of functions including locomotor activity, emotion, positive reinforcement, food intake, and endocrine regulation. The dopaminergic system has been extensively studied in the last thirty years mainly because its dysregulation has been linked to several neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases including Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia.1
All five dopamine receptors belong to the 7-transmembrane domain, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily.
Historically, the five receptors have been divided into two subfamilies based on pharmacological and structural considerations: the D1-like subfamily (that includes the D1 and D5 subtypes) and the D2-like subfamily (that includes the D2-, D3- and D4 subtypes).1
The D1-like receptors are coupled to Gs-type G proteins and enhance adenylate cyclase activity while the D2-like receptors are coupled to Gi-type G proteins and inhibit adenylate cyclase activity.1
The D3 receptor distribution in the brain is relatively restricted to limbic areas such as striatum, islands of Calleja and olfactory tubercle. In the periphery, it is expressed in the kidney particularly in proximal tubules.1
The exact physiological function of the D3 receptor remains to be fully elucidated. In studies using D3 receptor knockout mice, the most prominent dysfunction was the development of rennin-dependent hypertension. Potential roles in reinforcement and reward behaviors have also been suggested as well as roles in neuropsychiatric disorders such as drug abuse and schizophrenia.2
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
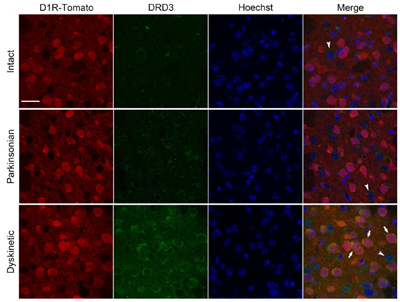
Expression of D3 dopamine receptor in mouse L-DOPA-treated brain.Immunohistochemical staining of free floating mouse coronal brain sections using Anti-D3 Dopamine Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#ADR-003), (1:100). DRD3 staining (green) is detected only following chronic L-DOPA treatment.Adapted from Solis, O. et al. (2017) Cereb. Cortex 27, 435. with permission of Oxford University Press.
