Overview
- Peptide (C)KKHEDESEAWLHR, corresponding to amino acid residues 414-426 of human DPP6 (Accession P42658). Extracellular, C-terminus.
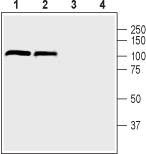 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysate:1,2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysate:1,2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with DPP6 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC146). Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate:1. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate:1. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:500).
2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with DPP6 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC146).
 Multiplex staining of DPP6 and KV4.2 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400) and Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:1000). A. DPP6 (green) is expressed in the CA3 rat hippocampal region. B. KV4.2 (red) is expressed in the same region. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization in neurons of the CA3 region (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of DPP6 and KV4.2 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400) and Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:1000). A. DPP6 (green) is expressed in the CA3 rat hippocampal region. B. KV4.2 (red) is expressed in the same region. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization in neurons of the CA3 region (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Expression of DPP6 in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-Cy3 antibody (red). Staining in the hippocampal CA3 region appears in interneurons (arrows). DAPI is used to stain nuclei (blue).
Expression of DPP6 in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-Cy3 antibody (red). Staining in the hippocampal CA3 region appears in interneurons (arrows). DAPI is used to stain nuclei (blue).
- Lin, L. et al. (2014) J. Biol. Chem. 289, 32153.
- Jerng, H.H. and Pfaffinger, P.J. (2012) PLoS One 7, e38205.
- Busek, P. et al. (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 36, 408.
- Lin, L. et al. (2013) Nat. Commun. 4, 2270.
- Liao, C. et al. (2013) Eur. J. Med. Genet. 56, 484.
- Prontera, P. et al. (2014) Neurogenetics 15, 237.
- Chettier, R. et al. (2014) PLoS One 9, e103968.
Dipeptidyl-peptidase 6 (DPP6) is a type II membrane glycoprotein1 which is a part of the dipeptydil aminopeptidase-like proteins (DPPLs) subfamily. It is an auxiliary glycoproteinic subunit of voltage-dependent K+ channel 4 (KV4.x), that has a short cytoplasmic domain, a long extracellular domain and a transmembrane domain. It regulates sub-threshold, A-type K+ currents, and is important for the enhancement and localization of KV4.2 channels2.
DPPLs are a subgroup of the larger prolyl oligopeptidase family. A loss-of-function mutation at their enzymatic serine renders them incapable of cleaving peptides. Notable DPPLs include DPP8, DPP9, and DPPIV – the latter is known to regulate several key functions in varied systems, ranging from immune to CNS1,3.
Alternative mRNA splicing of the DPP6 gene (part of the di-genic DPLP group that also consists DPP10) gives rise to several isoforms that differ in their N-terminal (DPP6a, DPP6K, DPP6S, DPP6L DPP6E)4.
DPP6 proteins are widely expressed throughout both of the nervous systems – albeit much more predominantly in the CNS - and are known to play a major role in neurogenesis and neurodevelopment5.
Deletion mutations and haplo-insufficiency of the DPP6 gene has been shown to be associated with autism spectrum disorder, Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, dominant microcephaly and mental retardation5,6. Endometriosis – a condition characterized by extra-uteral endometrial glands that affects one tenth of fertile women population – has been linked with DPP6 in genome wide associations studies (GWASs)7.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope and is thus ideal for detecting the protein in living cells. It has been designed to recognize DPP6 from rat, mouse, and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse brain sections.
Shiotani, H. et al. (2019) Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 94, 32.
