Overview
- Peptide (C)KKHEDESEAWLHR, corresponding to amino acid residues 414-426 of human DPP6 (Accession P42658). Extracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain lysate (1:200-1:1000) and human SH-SY5Y cell lysate (1:500-1:2500).
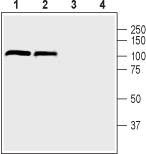 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysate:1,2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysate:1,2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with DPP6 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC146). Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate:1. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysate:1. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:500).
2. Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with DPP6 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC146).
- Mouse and rat brain sections (1:400).
Dipeptidyl-peptidase 6 (DPP6) is a type II membrane glycoprotein1 which is a part of the dipeptydil aminopeptidase-like proteins (DPPLs) subfamily. It is an auxiliary glycoproteinic subunit of voltage-dependent K+ channel 4 (KV4.x), that has a short cytoplasmic domain, a long extracellular domain and a transmembrane domain. It regulates sub-threshold, A-type K+ currents, and is important for the enhancement and localization of KV4.2 channels2.
DPPLs are a subgroup of the larger prolyl oligopeptidase family. A loss-of-function mutation at their enzymatic serine renders them incapable of cleaving peptides. Notable DPPLs include DPP8, DPP9, and DPPIV – the latter is known to regulate several key functions in varied systems, ranging from immune to CNS1,3.
Alternative mRNA splicing of the DPP6 gene (part of the di-genic DPLP group that also consists DPP10) gives rise to several isoforms that differ in their N-terminal (DPP6a, DPP6K, DPP6S, DPP6L DPP6E)4.
DPP6 proteins are widely expressed throughout both of the nervous systems – albeit much more predominantly in the CNS - and are known to play a major role in neurogenesis and neurodevelopment5.
Deletion mutations and haplo-insufficiency of the DPP6 gene has been shown to be associated with autism spectrum disorder, Gilles de la Tourette syndrome, dominant microcephaly and mental retardation5,6. Endometriosis – a condition characterized by extra-uteral endometrial glands that affects one tenth of fertile women population – has been linked with DPP6 in genome wide associations studies (GWASs)7.
