Overview
- Peptide CKQGFLSSNGQNHFK, corresponding to amino acid residues 58-72 of human EMR1 (Accession Q14246). Extracellular, N-terminus.

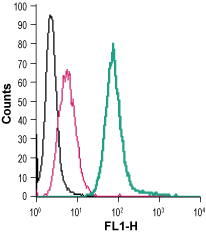 Cell surface detection of EMR1 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of EMR1 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-EMR1 (ADGRE1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#AER-051-F), (2.5 µg). Cell surface detection of EMR1 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of EMR1 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-EMR1 (ADGRE1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#AER-051-F), (2.5 µg).
- Legrand, F. et al. (2014) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 133, 1439.
- McKnight, A.J. and Gordon, S. (1998) J. Leukoc. Biol. 63, 271.
- Araç, D. et al. (2012) EMBO J. 31, 1364.
Human epidermal growth factor (EGF)–like module containing mucin-like hormone receptor 1 (EMR1) is a surface receptor with unknown function that belongs to the adhesion family of the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). This receptor is encoded by the ADGRE1 and like all GPCRs, contains seven transmembrane domains, an intracellular C-terminus and an extracellular N-terminus. The NH2 domain has six EGF-like domains.
Adhesion GPCRs share a long N-terminal extracellular sequences comprising multiple domains, separated from the transmembrane segments by a serine/threonine-rich domain, a feature reminiscent of mucin-like, single-span, integral membrane glycoproteins with adhesive properties1,2.
EMR1 protein is a homolog of F4/80, a murine protein that is widely being used as a marker of murine macrophage populations1.
Human EMR1 is exclusively expressed on mature eosinophils in the blood and bone marrow and in nasal polyps. Thus, EMR1 is considered to be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of eosinophilic disorders1,3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-EMR1 (ADGRE1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-051) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and live cell imaging applications. It recognizes an extracellular epitope and is thus ideal for detecting the receptor in living cells. It has been designed to recognize EMR1 from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Anti-EMR1 (ADGRE1) (extracellular)–FITC Antibody (#AER-051-F) is directly conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). The antibody can be used in immunofluorescent applications such as direct live cell flow cytometry.
