Overview
- Peptide (C)EELDRITEQTLFD, corresponding to amino acid residues 173-185 of rat ENaCα (Accession P37089). Extracellular loop.
- Rat and mouse kidney lysates (1:200).
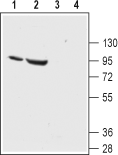 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) kidney lysates:1,2. Anti-ENaC α (SCNN1A) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-030), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) kidney lysates:1,2. Anti-ENaC α (SCNN1A) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-030), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-ENaC α (SCNN1A) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with ENaC α/SCNN1A (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC030).
- Mouse kidney sections (Wang, L. et al. (2015) J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 2678.).
The DEG/ENaC family consists of Na+ selective channels. They are characterized by 2 transmembrane domains with a large extracellular loop, important for channel activity and intracellular N-and C-termini which are important for channel gating and for interacting with regulatory proteins respectively1,2.
ENaC is localized to the apical side of polarized epithelial cells like those in the kidney, lung, and distal colon and is responsible for maintaining proper Na+ balance. This channel is formed by oligomerization of three subunits, α, β, and γ usually with the α2β1γ1 combination2,3. In addition, the α subunit which is essential for channel activity undergoes phosphorylation in its C-terminal by SGK1 (serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1) which is known to activate the channel at the plasma membrane4.
Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (PHA-1) has an early onset and is depicted by severe dehydration, hyponatremia and hyperkalemia5. One form of the pathology is characterized by mutations in α, β, and γ subunits5. The severity of the diseases depends on the loss of activity of the channel2.
