Overview
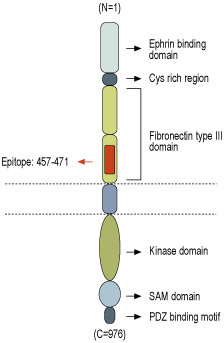
- Peptide (C)KKEPRQLELTWAGSR, corresponding to amino acid residues 457-471 of human EphA1 (Accession P21709). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with EphA1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER011).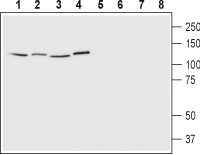 Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cell leukemia cells (lanes 1 and 5), human HeLa cervix adenocarcinoma cells (lanes 2 and 6), human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (lanes 3 and 7) and human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T cell leukemia cells (lanes 1 and 5), human HeLa cervix adenocarcinoma cells (lanes 2 and 6), human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (lanes 3 and 7) and human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with EphA1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER011).
 Expression of EphA1 in rat striatum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:300), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and Streptavidin-Cy3. A. EphA1 immunoreactivity (red) appears in striatal neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER011), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of EphA1 in rat striatum.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:300), followed by donkey anti-rabbit-biotin and Streptavidin-Cy3. A. EphA1 immunoreactivity (red) appears in striatal neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER011), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
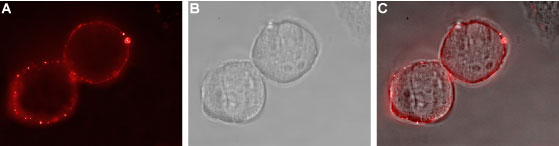 Expression of EphA1 in human MCF-7 cellsCell surface detection of EphA1 in live intact MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. Cells were stained with Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:25) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live image of the cells stained in A. C. Merge image of A and B.
Expression of EphA1 in human MCF-7 cellsCell surface detection of EphA1 in live intact MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. Cells were stained with Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011), (1:25) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live image of the cells stained in A. C. Merge image of A and B.
- Chen, Y. et al. (2012) Cell. Signal. 24, 606.
- Pasquale, E.B. (2008) Cell 133, 38.
- Pasquale, E.B. (2005) Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 462.
- Du, J. et al. (2007) Curr. Pharm. Des. 13, 2507.
- Wu, J. and Luo, H. (2005) Curr. Opin. Hematol. 12, 292.
- Ireton, R.C. and Chen, J. (2005) Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 5, 149.
- Noren, N.K. and Pasquale, E.B. (2007) Cancer Res. 67, 3994.
Eph receptors are the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). EphA receptors (EphA1-10) bind ephrinA ligands which are GPI-linked proteins and EphB receptors (EphB1-6) bind ephrinB ligands which are membrane protein with one transmembrane domain1,2. Within each subfamily, interactions between receptor and ligand are promiscuous. In addition, Eph receptors can also bind ephrins from the other class2. Forward and reverse signaling through Eph receptors is a unique characteristic to this RTK since ephrins are physically linked to the plasma membrane3.
Structurally, Eph receptors contain an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular C-terminal domain responsible for intracellular signaling1. Forward Eph receptor signaling involves autophosphorylation of the receptor via a tyrosine kinase domain, as well as phosphorylation of other proteins. Known effectors of the forward signaling include Src kinase and Ras/Rho GTPases2. Much less is known about the reverse signaling mediated by Eph receptors. Besides from acting independently, Eph receptors can also signal in concert with other receptors. For example, Eph receptors cooperate with FGF receptor, NMDA ligand-gated ion channel and chemokine G-protein coupled receptor2.
Biological activities attributed to the Eph receptor-ephrin signaling module include establishing neuronal connections, mediating neuronal plasticity and repair following neuronal injury2,4. Eph receptors may also have a role in the immune system5.
Eph receptors are expressed in the developing nervous system, and in the adult brain. It is also detected in the pancreas, intestine, bone and lymphocytes. In cancer cells, Eph receptors and ephrins are overexpressed2,6,7. They are also implicated in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease1.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-EphA1 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-011) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, live cell imaging, and indirect live cell flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize EphA1 from rat, mouse, and human samples.