Overview
- Peptide (C)HYLTAVGMGAKVELR, corresponding to amino acid residues 333 - 347 of human EphA2 (Accession P29317). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019). Western blot analysis of human U87-MG glioblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 5), human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 6), human LNCaP prostate adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human U87-MG glioblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 5), human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 6), human LNCaP prostate adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 7) and human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:200).
5-8. Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019).
 Expression of EphA2 in rat hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat hippocampal CA1 region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in neuronal profiles in both soma (vertical arrows) and apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). P = pyramidal layer, SO = stratum oriens, SR = stratum radiatum.
Expression of EphA2 in rat hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Staining in the rat hippocampal CA1 region, showed immunoreactivity (green) in neuronal profiles in both soma (vertical arrows) and apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). P = pyramidal layer, SO = stratum oriens, SR = stratum radiatum.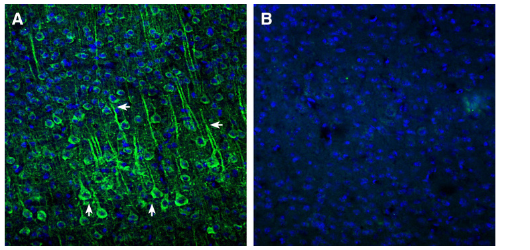 Expression of EphA2 in mouse cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. EphA2 immunoreactivity (green) appeared in neuronal profiles in both soma (vertical arrows) and apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of EphA2 in mouse cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. EphA2 immunoreactivity (green) appeared in neuronal profiles in both soma (vertical arrows) and apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with EphA2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-ER019), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Pasquale, E.B. (2008) Cell 133, 38.
- Zhou, Y. and Sakurai, H. (2017) Biol. Pharm. Bull. 40, 1616.
- Wykosky, J. and Debinski, W. (2008) Mol. Cancer. Res. 6, 1795.
- Tandon, M. et al. (2011) Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 15, 31.
Erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular receptor A2 (EphA2) is a tyrosine kinase that belongs to the Ephrin (Eph) family of receptors. Members bind to cell surface-associated Ephrin ligands on neighboring cells. This binding generates bidirectional signaling which is a major form of contact-dependent communication between cells1.
Eph receptors are divided into two classes, EphA and EphB, depending on the homology of their extracellular domains. Each extracellular domain is composed of a ligand-binding domain, Sushi domain, epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, and two fibronectin type-III repeats. Eph receptors also contain a transmembrane domain, juxtamembrane region, tyrosine kinase domain, sterile alpha motif (SAM) and postsynaptic density (PSD)-95 protein, Discs large, and Zona occludens tight junction protein (PDZ) domain-binding motif.
The interaction between Ephrin and the Eph receptor results in both “forward signaling” and “reverse signaling,” which are mediated by Eph receptor and Ephrin, respectively2. Forward signaling induces Eph receptor oligomer clustering, cross-phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on the juxtamembrane domain and activation loop and, consequently, activation of the kinase activity.
Eph receptor-ligand interactions mainly regulate cell proliferation and migration during development as well as tissue homeostasis, axon guidance, synapse plasticity, tissue remodeling, bone morphogenesis, and angiogenesis2.
EphA2 is expressed in normal epidermal cells and in various solid tumors, such as breast, ovary, prostate, pancreas, glioblastoma, neck, renal, lung, melanoma, bladder and other types of cancer2.
EphA2 expression in tumors is associated with a more aggressive cancer phenotype and correlates with tumor metastasis and poor patient outcome. In contrast, EphA2 also reduces cancer cell motility and proliferation and hence has both pro- and anti-oncogenic roles, depending on the cellular context3.
Due to its pivotal role in various diseases, EphA2 is an appealing drug target and research is performed in order to control its activity4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
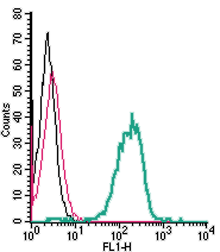
Anti-EphA2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AER-019) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of human EPHA2. The antibody can be used in western blot and live cell flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize EphA2 from rat, mouse, and human samples.